 Ignition Integration Guide
Ignition Integration Guide
Connect MaestroHub to Inductive Automation's Ignition Gateway for seamless tag browsing, reading, writing, and real-time subscriptions. This guide covers connection setup, function authoring, and pipeline integration.
Overview
The Ignition connector provides:
- WebSocket-based communication with the Ignition Gateway via the MaestroHub Ignition Module
- Interactive tag browsing to discover tags, folders, and UDT instances across all tag providers
- Efficient read/write operations for single or multiple tags with quality and timestamp information
- Real-time subscriptions that push tag value changes to your pipelines automatically
- Parameter templating for dynamic write operations with runtime value binding
The MaestroHub Ignition Module must be installed and running on your Ignition Gateway. The module provides the WebSocket endpoint and authentication required for MaestroHub connectivity.
Connection Configuration
Creating an Ignition Connection
Navigate to Connections → New Connection → Ignition and configure the gateway endpoint with the following fields.
Ignition Connection Creation Fields
1. Profile Information
| Field | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Connection Name | - | A unique, descriptive name for this connection (required, 1-100 characters) |
| Description | - | Optional description for this Ignition connection |
2. Gateway Configuration
| Field | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Host | - | Hostname or IP address of the Ignition Gateway (required, minimum 1 character) |
| Port | 45280 | WebSocket port for the MaestroHub Ignition Module (1-65535) |
| API Token | - | Authentication token generated from the Ignition Gateway's MaestroHub Module configuration page (optional, stored securely) |
Gateway URL Format
The full WebSocket URL is automatically constructed: ws://{host}:{port}
Example: ws://192.168.1.100:45280
3. Advanced Settings
| Field | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Default Tag Provider | default | Default tag provider when paths don't include a provider prefix (e.g., [default]) |
Common Tag Providers
default- Default tag providerSystem- System tag provider for gateway information
4. Timeout Configuration
| Field | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Connect Timeout (seconds) | 30 | Maximum time to wait when establishing the WebSocket connection (5-120 seconds) |
| Reconnect Interval (seconds) | 5 | Time to wait before attempting to reconnect after connection loss (1-60 seconds) |
| Request Timeout (seconds) | 30 | Maximum time to wait for browse, read, or write operations (1-120 seconds) |
5. Connection Labels
| Field | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Labels | - | Key-value pairs to categorize and organize this Ignition connection (max 10 labels) |
Example Labels
environment: production- Deployment environmentgateway: main- Gateway identifierlocation: plant-1- Physical locationsystem: scada- System type
- MaestroHub Module Required: The MaestroHub Ignition Module must be installed on the Ignition Gateway before creating this connection.
- Default Port: The standard MaestroHub module port is 45280.
- API Token: Generate the API token from the Ignition Gateway's MaestroHub Module configuration page. Leave empty in edit mode to keep the existing token.
- Default Provider: Used when tag paths don't specify a provider prefix (e.g.,
Motor1/Speeduses the default provider, while[System]Gateway/SystemNameuses the System provider). - Timeout Recommendations: Use a 30-second connect timeout for reliable connections. Adjust request timeout based on the number of tags being read or written.
- Security Note: API tokens are stored securely and used for authenticating WebSocket connections.
Function Builder
Creating Ignition Functions
Once the connection is saved:
- Go to Functions → New Function
- Choose Browse Tags, Read Tags, Write Tags, or Subscribe to Tags
- Select the Ignition connection profile
- Configure tag paths, values, and optional parameters

Author Ignition functions with tag browser, parameter templating, and validation
Browse Tags Function
Purpose: Browse the Ignition tag hierarchy to discover tags and folders. Navigate through providers, folders, UDT instances, and atomic tags.
Function Type ID: ignition.browse
Testable: Yes
Configuration Fields
| Field | Type | Required | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Browse Path | Text | No | "" (empty) | Tag path to browse. Leave empty to browse from root. Example: [default]Plant1/Line1 |
| Result Limit | Number | No | 1000 | Maximum number of nodes to return (1-10,000) |
Use Cases: Browse all tag providers, discover tags in a folder, find UDT instances, explore tag structure
UI Features
- Use the integrated tag browser to select a path
- Selecting a folder from the browser sets it as the starting browse path
- Browse results show node types (Folder, AtomicTag, UdtInstance, UdtType) and data types
Read Tags Function
Purpose: Read current values from one or more Ignition tags. Returns the value, quality, and timestamp for each tag.
Function Type ID: ignition.read
Testable: Yes
Configuration Fields
| Field | Type | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tag Paths | Array of Strings | Yes | Array of tag paths to read (minimum 1 tag, maximum 50 recommended). Example: [default]Motor1/Speed |
Input Methods
- Tag Browser: Select tags from the interactive browser
- Drag and Drop: Drag tags into the chip list area
- Manual Entry: Enter tag paths one per line in the textarea
Response Structure
Returns an array of tag values with:
path: Tag pathvalue: Current valuequality: Quality code (192 = Good, 0 = Bad, 64 = Uncertain)qualityName: Human-readable quality nametimestamp: ISO 8601 timestamp
Quality Codes
| Code | Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 192 | Good | Tag value is valid and reliable |
| 0 | Bad | Tag value is invalid or unreliable |
| 64 | Uncertain | Tag value may be questionable |
Use Cases: Read motor speed, get sensor values, check equipment status, read multiple tags at once
Write Tags Function
Purpose: Write values to one or more Ignition tags. Values support templating with ((parameter)) syntax for dynamic values from pipeline input.
Function Type ID: ignition.write
Testable: Yes
Configuration Fields
| Field | Type | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Write Operations | Array of Objects | Yes | Array of path/value pairs to write (minimum 1 operation) |
Write Operation Object
| Field | Type | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tag Path | Text | Yes | Tag path to write to. Cannot be empty or provider-only. Example: [default]Motor1/Setpoint |
| Value | Text | Yes | Value to write to the tag. Supports literal values (e.g., 1800), parameter templating (e.g., ((value))), or mixed (e.g., ((speed)) rpm) |
Parameter Templating
Use ((parameter_name)) syntax for dynamic values:
- Parameters are detected automatically from value fields
- Configure parameter types, defaults, and descriptions
- Parameters are filled in when testing or executing the function
Input Methods
- Tag Browser: Select tags to add new write entries with pre-filled paths
- Manual Entry: Add entries manually with the "Add Entry" button
- Remove Entries: Delete unwanted entries (minimum 1 entry required)
Path Validation
- Provider-only paths (e.g.,
[default]) are rejected - Full tag paths must be specified (e.g.,
[default]Motor1/Speed)
Use Cases: Set motor setpoint, update configuration values, write control commands, batch update multiple tags
Subscribe to Tags Function
Purpose: Creates subscriptions to Ignition tags. When tag values change, events are automatically pushed to connected pipelines. This function is event-driven and cannot be tested directly.
Function Type ID: ignition.subscribe
Testable: No (Event-driven)
Configuration Fields
| Field | Type | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tag Paths | Array of Strings | Yes | Array of tag paths to subscribe to (minimum 1 tag, maximum 50 recommended). Example: [default]Motor1/Speed |
Input Methods
- Tag Browser: Select tags from the interactive browser
- Drag and Drop: Drag tags into the chip list area
- Manual Entry: Enter tag paths one per line in the textarea
Event Structure
When tag values change, subscription events are pushed with:
functionId: ID of the subscription functionconnectionId: ID of the connectiontimestamp: Event timestamppayload.values: Array of changed tag values with path, value, quality, and timestamp
Use Cases: Monitor motor speed changes, track sensor value updates, detect status changes, real-time data streaming
- Subscribe functions are event-driven and cannot be tested directly
- Events trigger automatically when any subscribed tag value changes in the Ignition Gateway
- The connection must be active for subscriptions to work
Tag Path Format
Standard Format
Tag paths in Ignition follow the format: [provider]path/to/tag
Examples:
[default]Motor1/Speed[System]Gateway/SystemName[default]Plant1/Line1/Sensor_Temperature
Provider Prefix
- Optional in most cases (uses Default Tag Provider from connection settings)
- Required when accessing tags from non-default providers
- Format:
[providerName]
Path Separators
- Use forward slash
/to separate path segments - UDT instances and folders use the same separator
Node Types
| Node Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Folder | Container for organizing tags |
| AtomicTag | Individual tag with a value |
| UdtInstance | Instance of a User Defined Type |
| UdtType | Definition of a User Defined Type |
Data Types
Ignition supports the following data types:
- Boolean
- Int1 (8-bit integer)
- Int2 (16-bit integer)
- Int4 (32-bit integer)
- Int8 (64-bit integer)
- Float4 (32-bit float)
- Float8 (64-bit float)
- String
- DateTime
- DataSet
- Document
UI Features
Tag Browser
- Interactive Navigation: Browse the tag hierarchy in real-time
- Search Functionality: Find tags quickly
- Multi-Select: Select multiple tags at once (where applicable)
- Visual Indicators: Icons show node types and data types
- Drag and Drop: Drag tags from browser to configuration areas
Tag Chip List
- Visual Tag Management: See all selected tags as chips
- Remove Tags: Click the X on any chip to remove it
- Drag and Drop: Drag tags into the chip list area
- Validation: Real-time validation of tag paths
Parameter Configuration (Write Functions)
- Auto-Detection: Parameters in
((name))format are detected automatically - Type Configuration: Set parameter types (string, number, boolean, etc.)
- Default Values: Specify default values for parameters
- Descriptions: Add descriptions for each parameter
- Usage Tracking: See where each parameter is used
Using Parameters
Enclose dynamic values within ((parameterName)) to expose them for validation and runtime binding.
| Configuration | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Type | Ensure proper coercion | number, boolean, string, datetime |
| Required | Mark critical parameters | Required / Optional |
| Default Value | Provide safe baseline values | 1800, false |
| Description | Document usage for collaborators | "Motor setpoint in RPM", "Enable production mode" |
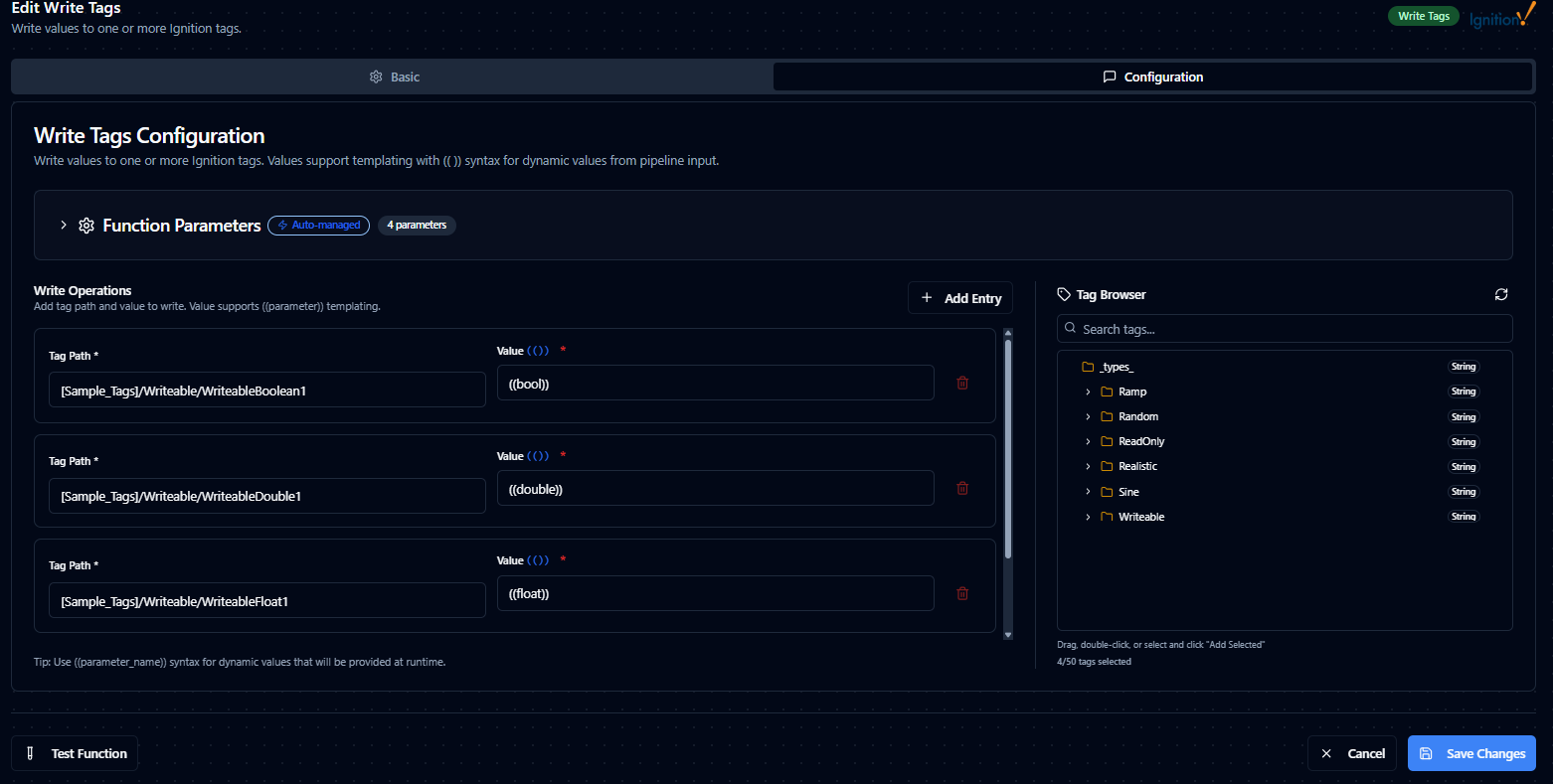
Parameter validation, defaults, and helper text for Ignition write functions
Pipeline Integration
Use the Ignition connection functions you configure here as nodes inside the Pipeline Designer to coordinate tag reads, writes, and subscriptions with downstream logic. Drag in the read, write, or subscribe node, bind parameters to upstream outputs or constants, and fine-tune retries or operator guidance without leaving the canvas.
For orchestration blueprints that combine Ignition with analytics, SQL, or notification steps, review the Connector Nodes page to understand how these nodes fit into broader automation strategies.
Ignition node with connection binding and parameter configuration
Common Use Cases
Production Data Collection
Poll tags for production counts, cycle times, and process variables, then push results to historians, databases, or analytics platforms.
Supervisory Control
Deliver validated setpoints or mode changes to the Ignition Gateway in response to business logic, alarms, or operator approvals.
Real-Time Monitoring
Subscribe to critical tags and trigger pipelines automatically when values change, enabling real-time alerting and event-driven automation.
Equipment Status Tracking
Read equipment status tags and forward the data to dashboards, MQTT topics, or REST APIs for centralized visibility across multiple systems.