Troubleshooting Guide
This comprehensive guide helps you troubleshoot issues in MaestroHub by explaining where to look and what information is available when you encounter problems. Whether you've just created a connection, configured a pipeline, or are investigating execution failures, this documentation will guide you through the key monitoring and diagnostic pages.
When to Use This Guide
Use this guide when you need to:
- Verify a new connection is working after creation
- Investigate pipeline execution failures or unexpected behavior
- Monitor system health and performance metrics
- Diagnose errors or warnings in your integrations
- Perform regular system health checks
System Logs
Navigation: System Management → Logs
Overview
The System Logs page provides centralized access to logs from all backend services in MaestroHub. This is your primary tool for detailed troubleshooting and understanding what's happening under the hood.
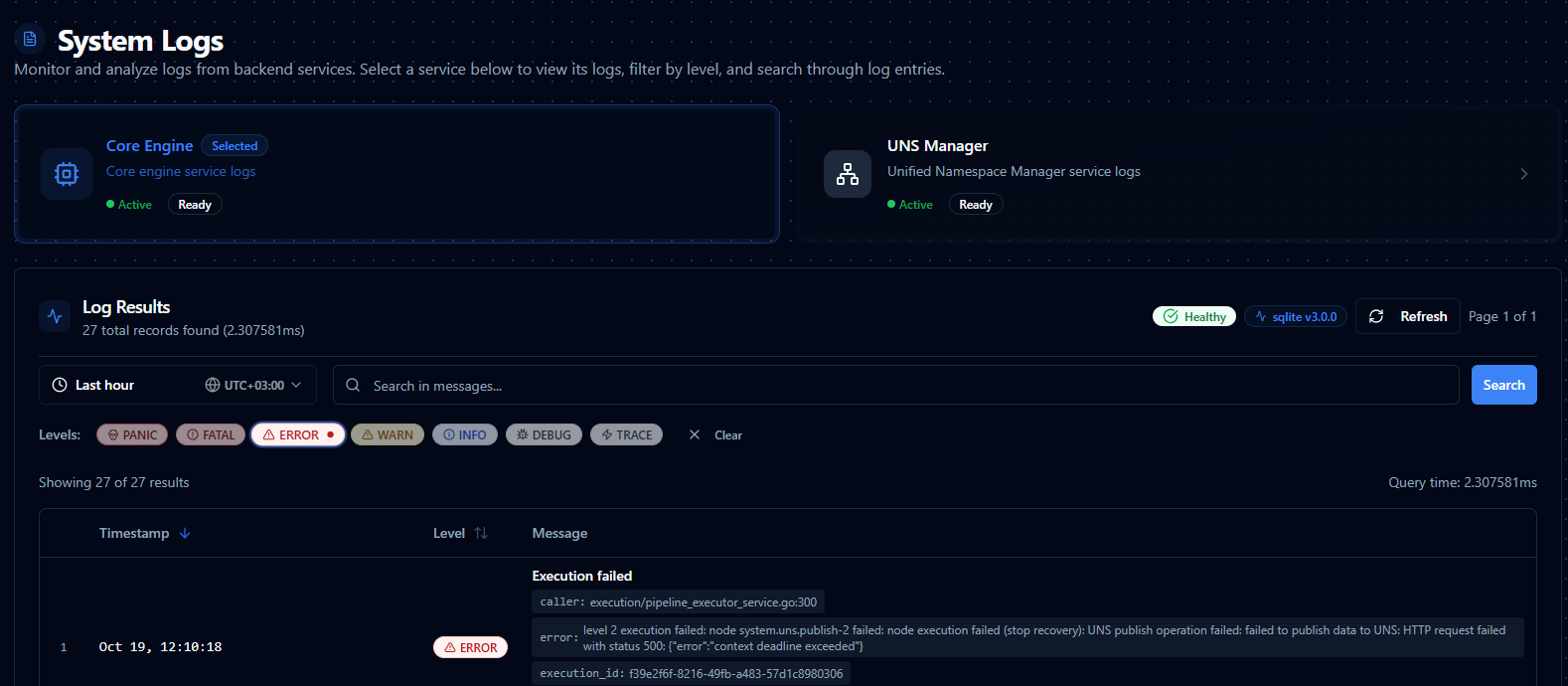
System Logs interface showing service selection, health status, and log results table.
System logs are available for the last 2 hours. This helps keep your workspace fast and responsive by automatically removing older logs after the retention period.
Service Selection
At the top of the page, choose which service's logs to view:
Core Engine Logs
- Main workflow engine operations
- Pipeline execution details
- Connection management
- Node operations and results
UNS Manager Logs
- Unified Namespace Manager activities
- Data integration processes
- Messaging operations
- Real-time data flows
Each service card displays:
- Service name and detailed description
- Current health status (Healthy or Unhealthy)
- Provider information (SQLite, Elasticsearch, ZincSearch, etc.)
- Quick access button to view logs
Health Status Indicators
Healthy Status
The service is fully operational with all systems functioning correctly. Log provider is accessible and logs are being collected and stored properly. This is the expected normal state.
Unhealthy Status
There may be service disruptions or issues. The log provider might be unavailable or experiencing connectivity problems. Logs may not be accessible or incomplete. Investigate immediately if you see this status.
Log Viewer Interface
Time Range Selector
Choose the appropriate time window for your investigation:
- Last 15 minutes: Quick check for recent activity and immediate issues
- Last hour: Standard troubleshooting window for most scenarios
- Last 6 hours: Broader investigation for intermittent issues
- Last 24 hours: Full-day analysis for pattern recognition
- Custom range: Specify exact start and end times for precise investigation
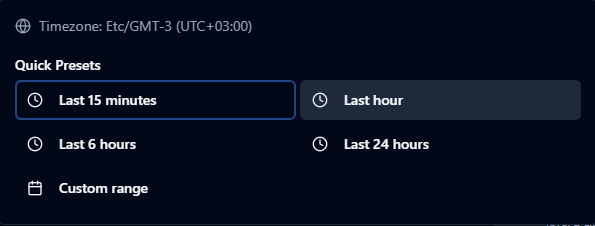
Time range presets and custom range options for filtering logs.
Search and Filters
Global Search allows you to search across all log fields simultaneously. This is useful for finding specific error messages, IDs, or keywords. For example, search for a connection ID to find all related log entries.
Advanced Filters help narrow down logs with multiple criteria:
Field Options:
- Level: Log severity (ERROR, WARN, INFO, DEBUG, etc.)
- Message: Log message content
- Source: Origin of the log entry
- Timestamp: When the event occurred
- Custom fields: Service-specific attributes
Operator Options:
- Equals: Exact match for specific values
- Not equals: Exclude specific values
- Contains: Text search within field content
- Is one of: Match any value in a list
- Is not one of: Exclude multiple values
Common Filter Examples:
Show only errors: Set level equals ERROR to focus on critical issues.
Exclude debug logs: Set level not equals DEBUG for cleaner output.
Find connection errors: Set message contains "connection failed" to identify connectivity issues.
Multiple statuses: Set level is one of ERROR,WARN to see warnings and errors together.
Log Table Columns
Timestamp
Shows when the log entry was created. Use this to understand timing of events and sequence of operations. Essential for correlating related events.
Level
Indicates severity of the log entry:

Log level chips showing PANIC, FATAL, ERROR, WARN, INFO, DEBUG, and TRACE options.
- FATAL and PANIC: Critical system failures requiring immediate attention. These indicate severe problems that may stop service operation.
- ERROR: Operation failures, failed connections, and execution errors. These need investigation and resolution.
- WARN: Potential issues, deprecation warnings, and retry attempts. Monitor these to prevent future problems.
- INFO: Normal operations, successful actions, and status updates. These confirm expected behavior.
- DEBUG: Detailed diagnostic information useful for development and deep troubleshooting.
- TRACE: Very detailed execution traces for low-level debugging.
Message
Primary log message containing error descriptions, status updates, and operation details. This is usually the most informative field.
Additional Fields
Custom fields specific to each log entry may include:
- Connection IDs and names
- Pipeline IDs and names
- Execution IDs
- Node names and types
- Duration measurements
- Error details
- Request/response data
Sorting and Pagination
Click on column headers to sort data. Click timestamp to see most recent or oldest entries first. Click level to group by severity. Toggle between ascending and descending order with additional clicks.
The bottom of the table shows current page number, total records found, and query execution time. Use the Load More button to retrieve additional pages if available.
Common Use Cases
After Creating a Connection
- Switch to Core Engine Logs service
- Set time range to Last 15 minutes
- Add filter: message contains "connection"
- Look for "Connection established successfully" at INFO level
- Check for connection test results
- Investigate any ERROR level messages immediately
After Pipeline Execution Failure
- Switch to Core Engine Logs service
- Set time range covering the execution period
- Add filter: level equals ERROR
- Search for your pipeline ID or name
- Look for node execution errors, connection failures, validation errors, or timeout messages
- Expand error entries to see full stack traces and context
Monitoring UNS Integrations
- Switch to UNS Manager Logs service
- Set time range to Last hour
- Filter by your integration type or topic
- Look for message publishing confirmations, message receiving confirmations, connection status changes, data transformation logs, and MQTT or AMQP broker connection status
Troubleshooting Tips
If logs are not showing:
- Check the health status indicator at the top
- Verify the time range includes when the event occurred
- Clear all filters and try a broader search
- Ensure the correct service is selected
- Refresh the page to reload data
If too many logs:
- Add more specific filters to narrow results
- Narrow the time range to focus on relevant period
- Use the global search for specific IDs or keywords
- Focus on ERROR and WARN levels first to identify critical issues
Understanding Error Messages:
Most error logs include additional context fields:
- Error field: Detailed error description and stack trace
- Connection ID: Which connection had the issue
- Pipeline ID: Which pipeline was executing
- Node ID: Which specific node failed
- Execution ID: Specific execution instance identifier
- Duration: How long the operation took before failing
Execution History
Navigation: Orchestrate → Pipelines → Select Pipeline → Execution History tab
OR
All Executions View: Orchestrate → Execution History (for all pipelines)
Overview
The Execution History page shows all past and current runs of your pipelines. This is essential for understanding pipeline performance, debugging failures, and tracking execution patterns over time.
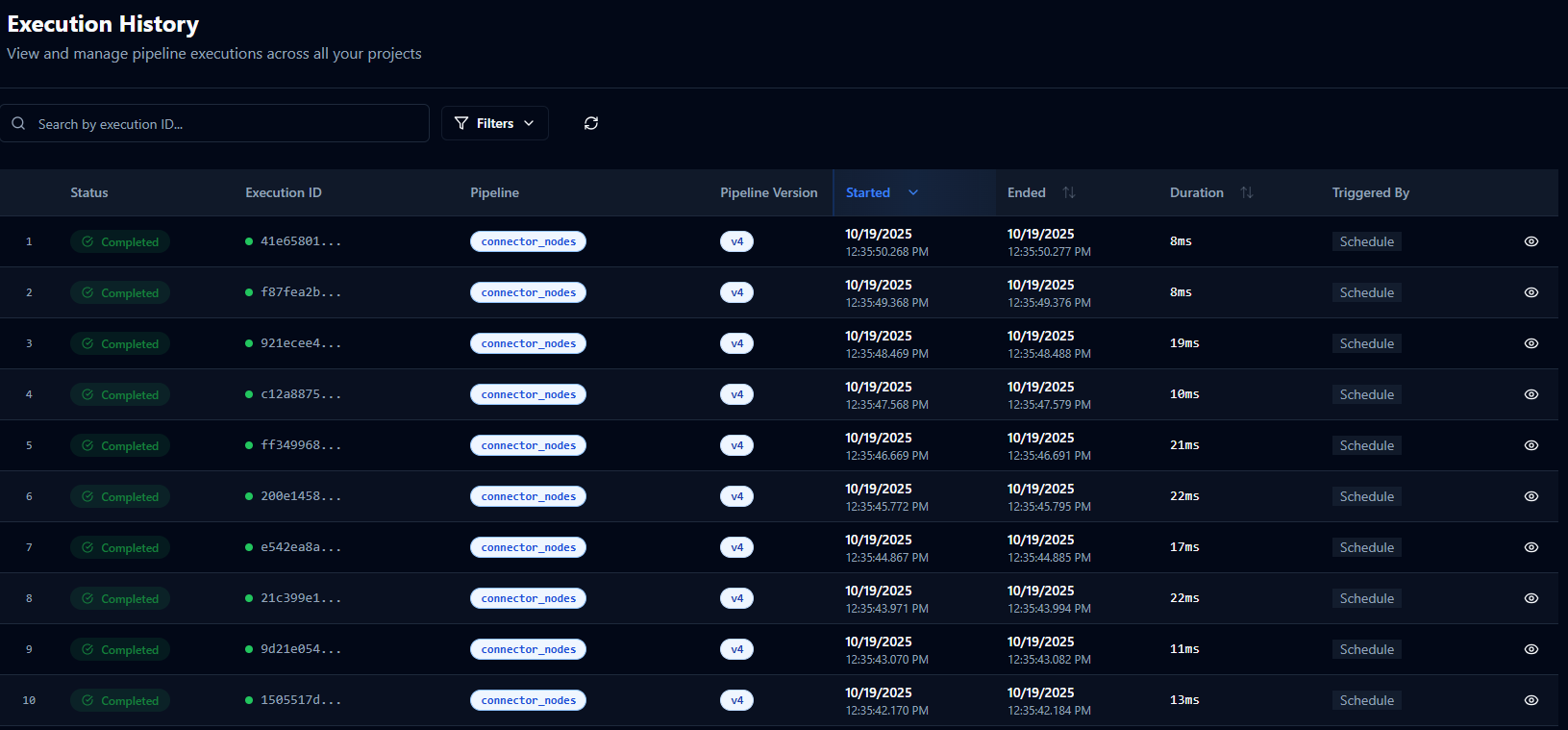
Execution History list with search bar, filters, and recent pipeline runs.
Quick Statistics
| Metric | What it highlights | When to focus |
|---|---|---|
| Completed | Executions that finished without errors and ran every node as expected. | Validate overall stability and monitor success rate trends. |
| Failed | Executions that ended with errors or aborted nodes. | Prioritize triage and link back to logs or pipeline changes. |
| Running | Pipelines that are currently in progress. | Track long-running jobs and decide if intervention is needed. |
Execution Table Details
| Column | Description | Tips |
|---|---|---|
| Execution ID | Unique UUID for each run with a quick copy icon for sharing. | Include in support tickets or search the System Logs for the same ID. |
| Pipeline | Name of the pipeline that executed; in the All Executions view it doubles as a filter shortcut. | Click the name to scope the list to that pipeline only. |
| Status | Color-coded badge indicating the execution outcome. | See the status reference below to decide next actions. |
| Start Time | Timestamp for when the run began. | Sort ascending to analyze historical patterns or descending for recent activity. |
| End Time | Timestamp for completion or In Progress for active runs. | Combine with duration to spot timeouts or stuck executions. |
| Duration | Total time from start to finish in human-readable format. | Sort to identify slow pipelines and correlate with configuration changes. |
| Triggered By | Origin of the run (Schedule, Manual, API, etc.). | Helps validate automations and unexpected triggers. |
Status reference
| Status | Meaning | Suggested follow-up |
|---|---|---|
| Completed | All nodes finished successfully. | No action needed; review duration for optimization if desired. |
| Failed | One or more nodes ended with errors. | Open details to inspect failing node and remediate. |
| Running | Execution in progress with animated indicator. | Monitor duration or cancel if it exceeds expected runtime. |
| Pending | Run is queued and waiting to start. | Check worker capacity or scheduling constraints if it remains pending. |
| Cancelled | Execution was stopped manually or by policy. | Confirm whether a rerun is required after the intervention. |
| Paused | Execution halted awaiting user input or external signal. | Resume or cancel after resolving the blocking condition. |
| Partial | Mixed outcome—some nodes succeeded, others failed. | Investigate partial nodes and plan targeted reruns. |
Actions Available
| Action | Availability | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| View Details | All executions. | Opens the execution drawer with node-level output, timings, and errors for deep troubleshooting. |
| Rerun | Completed, Failed, or Cancelled executions. | Launches the same pipeline configuration again—ideal after applying a fix. |
| Cancel | Running or Pending executions. | Stops an in-flight run that is stuck, misconfigured, or no longer needed. |
Filtering and Searching
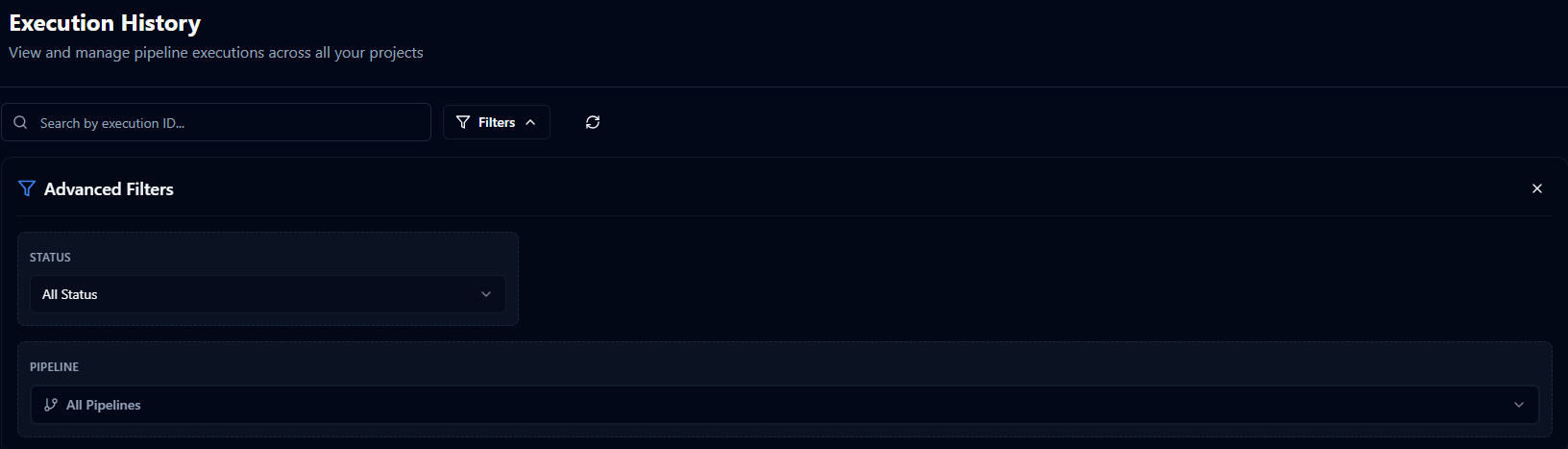
Advanced filters with status, pipeline selection, and search controls.
Status Filter Dropdown
Filter by execution status: All, Completed, Failed, Running, Cancelled, or Partial. Great for focusing on failures only or monitoring active executions.
Pipeline Filter
In All Executions view, select specific pipeline from dropdown. Shows pipeline name and ID. Filters table to show only that pipeline's executions.
Execution ID Search
Enter partial or full execution ID in search box. Real-time filtering as you type. Useful when you have a specific execution ID from logs or notifications.
Sorting
Click column headers to sort: Start Time, End Time, or Duration. Toggle between ascending and descending order. Identify patterns like slowest executions or most recent failures.
Viewing Detailed Results
Click View Details to open the execution results dialog with a comprehensive tabbed interface.
Detailed logs for executions older than 2 hours are removed automatically after the retention period. This helps keep your workspace fast and responsive. You can still access high-level information for older executions, including execution status, duration, and basic execution metadata.
Overview Tab
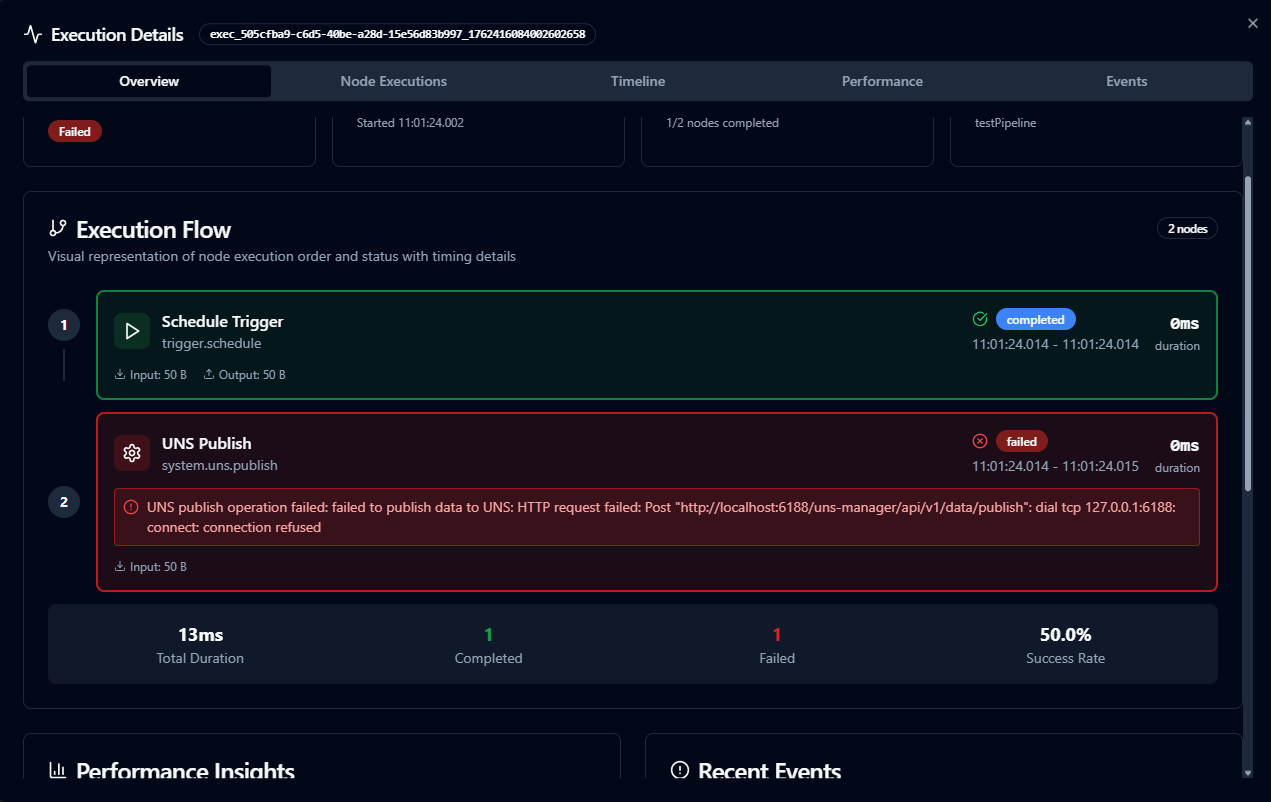
Execution details showing Overview tab with execution summary, node flow, performance insights, and error information.
The Overview tab provides a quick diagnostic summary ideal for troubleshooting:
- Execution Summary: Status, duration, trigger type, and key metrics at a glance
- Visual Execution Flow: Chronological node timeline showing execution order, status, and dependencies
- Performance Insights: Identifies slowest nodes and bottlenecks for optimization
- Error Summary: Highlights failed nodes with error messages for quick triage
- Quick Actions: Navigate directly to detailed analysis tabs
Additional Tabs for Deep Analysis
- Node Executions: Expandable node-by-node breakdown with input/output data, timing details, and error messages
- Timeline: Chronological event stream with filtering to track execution sequence and delays
- Performance: Node-level metrics showing execution time, data throughput, and bottleneck analysis
- Events: Raw event log with detailed timestamps and system-level debugging information
Common Use Cases
Finding Recent Failures
- Open Execution History for your pipeline
- Click Status Filter dropdown and select Failed
- Click on the most recent failed execution
- Click View Details to see which node failed and why
- Read the error message and check input data
- Fix the issue in pipeline or connection configuration
- Click Rerun to verify the fix
Monitoring Running Executions
- Go to Execution History page
- Look for Running status with animated badge
- Note the start time to track duration
- If taking too long or stuck, click Cancel to stop it
- Refresh periodically to see status updates
- Investigate in System Logs if execution seems stuck
Analyzing Performance
- Open Execution History for your pipeline
- Click Duration column header to sort by execution time
- Identify slowest executions at the top
- Click View Details on slow executions
- Review node-by-node timing in the results
- Identify bottleneck nodes
- Optimize slow nodes or connections
Tracking Execution Patterns
- Set time range to wider window (hours or days)
- Look at frequency of executions over time
- Check success versus failure ratio
- Identify patterns such as failures at specific times
- Correlate with system events or external factors
Troubleshooting Tips
If an execution failed:
- Click View Details on the failed execution
- Look at the Node Execution Timeline to see progress
- Find the red (failed) node in the list
- Read the error message in the node details carefully
- Check the node's input data for formatting or content issues
- Go to System Logs with the execution ID for more detailed error information
- Fix the issue (connection settings, node configuration, or data format)
- Click Rerun to try again and verify the fix
If an execution is stuck:
- Check the start time to determine how long it's been running
- Click View Details to see which nodes have completed
- The last completed node shows where execution is stuck
- Check System Logs for that node's activity and any errors
- If truly stuck with no progress, click Cancel to terminate
- Investigate the problematic node configuration before rerunning
If you can't find an execution:
- Check the time range to ensure it covers when execution occurred
- Clear any status filters that might be hiding it
- Use the Execution ID search if you have the specific ID
- Try the All Executions view if you're not sure which pipeline
- Check System Logs to confirm the execution was actually triggered
Connection Status
Navigation: Connect → Connections
Overview
The Connection Status column in the connections table shows real-time health and connectivity information for each configured connection. This helps you quickly identify connection problems before they affect pipeline executions.
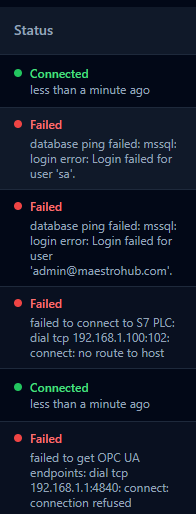
Connection status column with mixed healthy and failed endpoints.
Status Indicators
Each connection row displays two key indicators:
Connection Status Indicator
Visual indicator showing operational state:
| Status | Description |
|---|---|
| Connected | Active connection is established and operational; green indicator shows healthy state. |
| Disconnected | Not currently connected to the target system; gray indicator shows inactive state. |
| Connecting | Actively attempting to establish a connection; yellow indicator shows in-progress state. |
| Failed | Connection attempt failed due to an error; red indicator shows problem state. |
| Loading | Status is being checked by the system; pulsing gray indicator shows the check in progress. |
| Unknown | Status not yet determined or unavailable; gray indicator shows an indeterminate state. |
Health Status Text
Below the connection status, you'll see health information:
| Health status | Description |
|---|---|
| Healthy | Connection tested successfully and is fully operational; green text confirms the working state. |
| Unhealthy | Connection problems detected and it may not work properly; red text warns of issues. |
| Unknown | Health check not yet performed or unavailable; gray text shows an undetermined state. |
Understanding Each Status
Connected and Healthy
This is the ideal state. Connection is established and working properly. Connection pool is active and ready. Health check passed successfully. The connection is ready to use in pipeline executions without issues.
No action is needed. The connection is fully operational and reliable.
Connected and Unhealthy
Connection is established but health check failed. May be experiencing intermittent issues. Could be slow to respond or have authentication problems. May have permission issues preventing certain operations.
Recommended Actions:
- Click Test Connection button to recheck status
- Review System Logs for detailed error messages
- Check if credentials are still valid and not expired
- Verify network connectivity between systems
- Confirm target system is operational and accepting connections
Disconnected
No active connection to the target system exists. Connection pool is empty. Either not currently in use, failed to establish, or first connection not yet attempted.
Recommended Actions:
- Click Test Connection to establish connection
- If test fails, check connection configuration carefully
- Review System Logs for connection errors and details
- Verify credentials and network settings are correct
Connecting
Actively attempting to establish connection. Authentication is in progress. Initial handshake with target system is occurring.
Wait a few seconds for connection to establish normally. If stuck for more than 30 seconds, there may be network issues. Check System Logs for timeout or connection errors.
Failed
Connection attempt failed due to errors. Possible causes include authentication failure, network unreachable, target system not responding, or incorrect configuration.
Recommended Actions:
- Click Test Connection to see detailed error message
- Review error message in test result dialog carefully
- Check for common issues:
- Wrong credentials (username, password, or token)
- Incorrect host address or port number
- Firewall blocking connection between systems
- SSL or TLS certificate validation issues
- Target service is down or unavailable
- Check System Logs for full error details and stack traces
- Edit connection configuration to fix identified issues
- Test again after making changes to verify fix
Connection Actions
Test Connection Button
Manually trigger connection test to verify connectivity. Performs complete health check. Shows detailed result dialog with success or failure status, response time measurement, error messages if any issues occurred, and connection details for verification.
Edit Connection
Click connection name or Edit button to access configuration. Modify connection settings as needed. Update credentials if they've changed or expired. Always test connection before saving changes.
View Functions
For database connections, see available stored procedures and functions. Test function execution directly. Review function metadata and parameters.
Connection Status in Pipeline Context
Before Pipeline Execution
Ensure all connections used in the pipeline are showing Healthy status. Test any connections showing Unknown status to verify they work. Fix any Failed or Unhealthy connections before running pipeline to avoid execution failures.
During Pipeline Execution
Connection status is checked when each node executes. If connection is unhealthy, node execution will fail immediately. Error message will clearly indicate connection problem. Check Execution History for specific error details.
After Pipeline Failure
Check if pipeline used any unhealthy connections that may have caused failure. Verify connection status in Connect page. Test connection to confirm it's working properly. Rerun pipeline after fixing connection to verify solution.
Pipeline Metrics
Navigation: Overview
Overview
The Pipeline Metrics dashboard provides real-time visibility into your workflow and pipeline execution activity across MaestroHub. Use these metrics to monitor system health, detect anomalies, and verify that pipelines are running as expected.
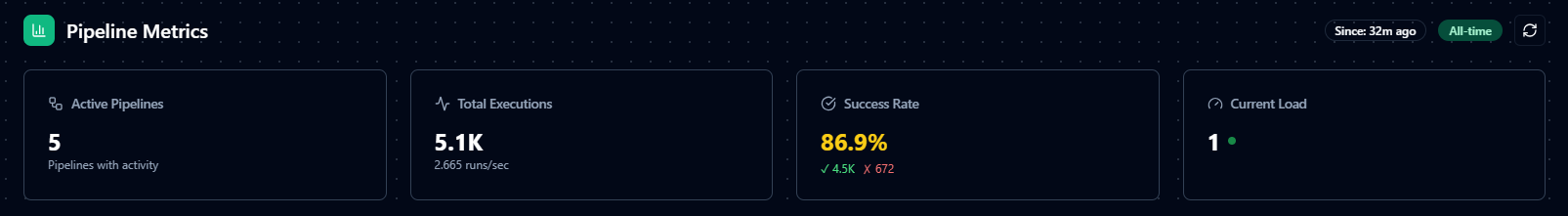
Pipeline Metrics dashboard showing real-time execution metrics and system activity.
Auto-Refresh Behavior
Metrics automatically update every 60 seconds to provide near real-time data. A "Next refresh in" indicator shows countdown to the next update. Use the refresh button in the top-right corner for immediate manual updates.
The Four Key Metrics
The overview dashboard displays four metric cards that provide a comprehensive snapshot of your pipeline ecosystem:
| Metric | What It Shows | When to Monitor |
|---|---|---|
| Total Pipelines | Total count of all pipelines configured in your system across all environments. | Track growth of your automation footprint and verify new pipelines appear after creation. |
| Success Rate | Percentage of successful pipeline executions vs. total runs. Shows as "X.X%" with a subtitle displaying "Y of Z runs" to give you the exact counts. The card color changes based on performance: Green (≥95%), Yellow (80-94%), Red (<80%). | Critical health indicator—monitor continuously to catch reliability issues early. Investigate immediately if rate drops below 80%; review patterns if below 95%. |
| Active Now | Combined count of currently running and queued pipeline executions. Shows breakdown as "X running, Y queued" in the subtitle. | Real-time system load indicator—essential during deployments or when investigating performance issues. Check for stuck pipelines or resource constraints if unexpectedly high. |
| Throughput | Pipeline execution rate measured in executions per second (e.g., "2.45/s"). Indicates overall system processing velocity. | Monitor during load testing or to understand system capacity utilization. Compare against baseline to detect performance degradation or unusual activity spikes. |