Nodes: Building Blocks of Automation
Nodes are the fundamental building blocks of MaestroHub Pipelines. Each node represents a specific action, logic, or integration point in your workflow. By connecting nodes together, you create sophisticated automation without writing code.
The node library is organized into categories based on functionality and continues to grow with new integrations and capabilities added regularly.

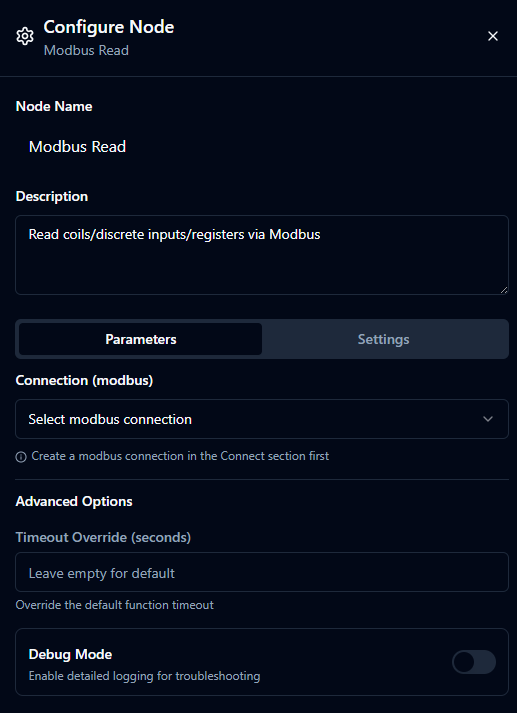
Modbus Read
MSSQL Query
REST Request

UNS Publish
Merge

JavaScript
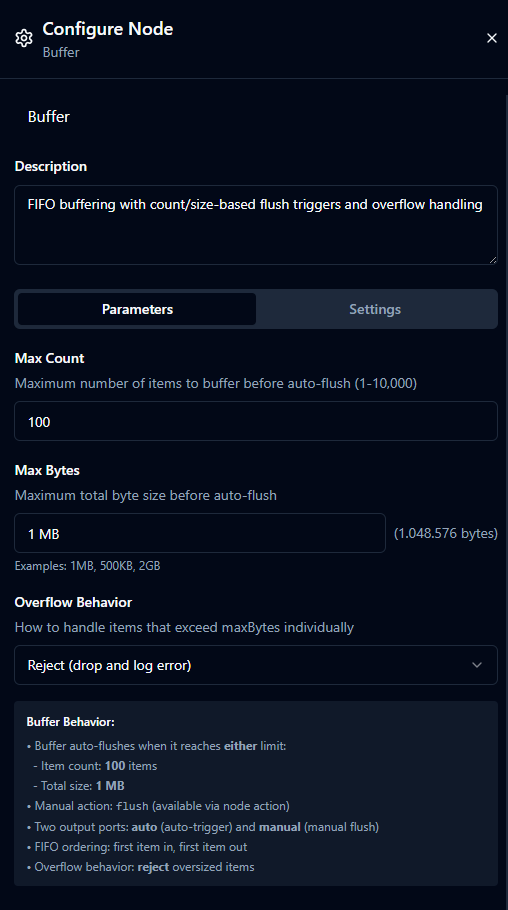
Node Configuration
When you select a node on the canvas, the configuration panel opens on the right side. While the layout follows familiar patterns for clarity—such as tabs like Parameters, Content, Options, or Settings—the exact tabs and fields vary by node type so each node can surface its own specialized options.
Error Handling Strategies
Choose the appropriate error handling strategy based on your business requirements:
- Stop Pipeline: Critical operations where failure should halt the entire workflow (e.g., payment processing, data validation)
- Continue Execution: Non-critical operations where the workflow can proceed despite failures (e.g., optional logging, notifications)
- Retry Node: Transient issues that may resolve with retry attempts (e.g., network calls, temporary service unavailability)
Configuration Best Practices
- Naming: Use clear, business-meaningful names that describe the node's action
- Documentation: Always add notes for complex logic to help team members understand the workflow
- Error Handling: Set appropriate error strategies based on operation criticality
- Validation: Test node configurations before deploying to production
- Consistency: Follow your team's naming conventions across all pipelines
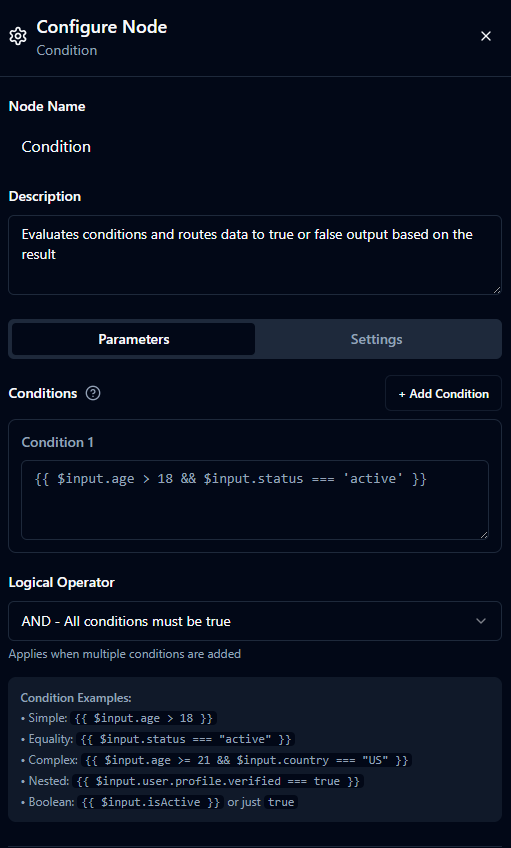
Expression Variables
Nodes share a powerful expression engine that exposes context objects under well-known variables. Understanding each scope helps you keep expressions concise while still tapping into the full runtime context.
| Variable | Purpose | Ideal usage | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
$input | Shortcut to the single inbound packet when the node has exactly one incoming port. | Simplify straightforward chains where only one payload feeds the node. | {{ $input.user.age }} |
$inputs | Map of all inbound ports keyed by name. | Required for fan-in scenarios (Merge, Condition) or custom port IDs. | {{ $inputs.userData.age }} |
$node | Metadata about the node currently executing (ID, name, run counts, timestamps). | Diagnostics, tagging outputs, loop-aware behavior. | {{ $node.executionCount }} |
$nodes | Snapshot of other nodes’ published outputs or state. | Cross-node coordination without extra wiring; cached lookups. | {{ $nodes.validator.output.valid }} |
$pipeline | Static pipeline-level configuration and metadata. | Environment-specific branching, feature toggles, traceability. | {{ $pipeline.strategy }} |
$execution | Metadata tied to the current run (triggering user, run ID, permissions). | Per-run personalization, auditing, permission checks. | {{ $execution.user.role }} |
$history | Results from previous executions of named nodes (length, outcomes, timing). | Trend detection, guardrails, adaptive retries; verify node support first. | {{ $history.apiCall.executions.length }} |
$trigger | Details about the pipeline trigger (type, payload, headers, schedule). | Branch logic by trigger type or propagate trigger metadata downstream. | {{ $trigger.type }} |
Tip: Variables can be combined—for example, fall back from $input to $inputs when branching, or blend $pipeline.strategy with $execution data to adjust behavior mid-run.
Popular Nodes to Get Started
Explore commonly used nodes to understand how they work in your pipelines:
- Schedule Trigger - Automate workflows with time-based triggers using cron expressions
- Condition - Branch your workflow based on data conditions and business rules
- Set - Transform and manipulate data fields as they flow through your pipeline
- JavaScript - Execute custom logic for complex business requirements
- Connector Nodes - Integrate with external systems like Modbus, MQTT, databases, and APIs
You can discover all available nodes organized by category in the sidebar, or directly from the Pipeline Designer's node panel.
The MaestroHub Advantage: Powerful automation building blocks that anyone can master, backed by enterprise-grade reliability.