Ignition trigger node
Ignition Trigger Node
Overview
The Ignition Trigger Node automatically initiates MaestroHub pipelines when tag values change in Inductive Automation's Ignition Gateway. Unlike polling-based approaches, this trigger provides real-time event-driven automation with intelligent debouncing—multiple rapid tag changes within 100ms are aggregated into a single pipeline execution with the latest values for all affected tags.
Core Functionality
What It Does
Ignition Trigger enables real-time, event-driven pipeline execution by:
1. Event-Driven Pipeline Execution
Start pipelines automatically when Ignition tag values change, without manual intervention or polling. Perfect for process monitoring, alarm handling, and real-time data flows.
2. Intelligent Debouncing
Multiple tag changes within a 100ms window are automatically aggregated into a single event, preventing excessive pipeline executions while ensuring you receive the latest values for all changed tags.
3. Automatic Subscription Management
Subscriptions are created and cleaned up automatically—no manual subscription management required. The system handles connection lifecycle and resubscription after reconnections.
4. Aggregated Tag Data
All tag values that changed during the debounce window are provided in a single array, making it easy to process multiple related tag changes together.
Debounce Behavior
How Debouncing Works
The Ignition Trigger uses a 100ms fixed debounce window to aggregate rapid tag changes:
- First Change: When the first tag value change occurs, a 100ms timer starts
- Subsequent Changes: Any additional tag changes within this window update the buffer with the latest values
- Timer Expires: After 100ms, the trigger fires once with an array containing the latest values for all tags that changed
- Next Window: The process repeats for the next set of changes
Benefits of Debouncing
| Scenario | Without Debouncing | With Debouncing |
|---|---|---|
| 10 rapid tag changes | 10 separate pipeline executions | 1 pipeline execution with all 10 tag values |
| Burst updates | Pipeline overload, potential queueing | Smooth processing with aggregated data |
| Related tag changes | Process tags individually, lose context | Process all related changes together |
The 100ms debounce window is fixed and cannot be configured. This value provides an optimal balance between responsiveness and aggregation for most industrial automation scenarios.
Reconnection Handling
MaestroHub automatically handles connection disruptions to ensure reliable tag monitoring.
Automatic Recovery
When an Ignition connection is lost and restored:
- Connection Lost: The system detects the disconnection automatically
- Connection Restored: Subscriptions are automatically re-established within seconds
- Transparent Recovery: Pipelines continue to receive tag changes once the connection is restored—no manual intervention required
What This Means for Your Workflows
| Scenario | Behavior |
|---|---|
| Brief network interruption | Automatic resubscription after reconnection |
| Gateway restart | Subscriptions automatically restored when gateway comes back online |
| MaestroHub restart | All triggers for enabled pipelines are restored on startup |
While the trigger automatically reconnects, tag changes that occur during the disconnection period may be missed. For critical data, consider implementing a complementary polling mechanism or using Ignition's built-in store-and-forward capabilities.
Configuration Options
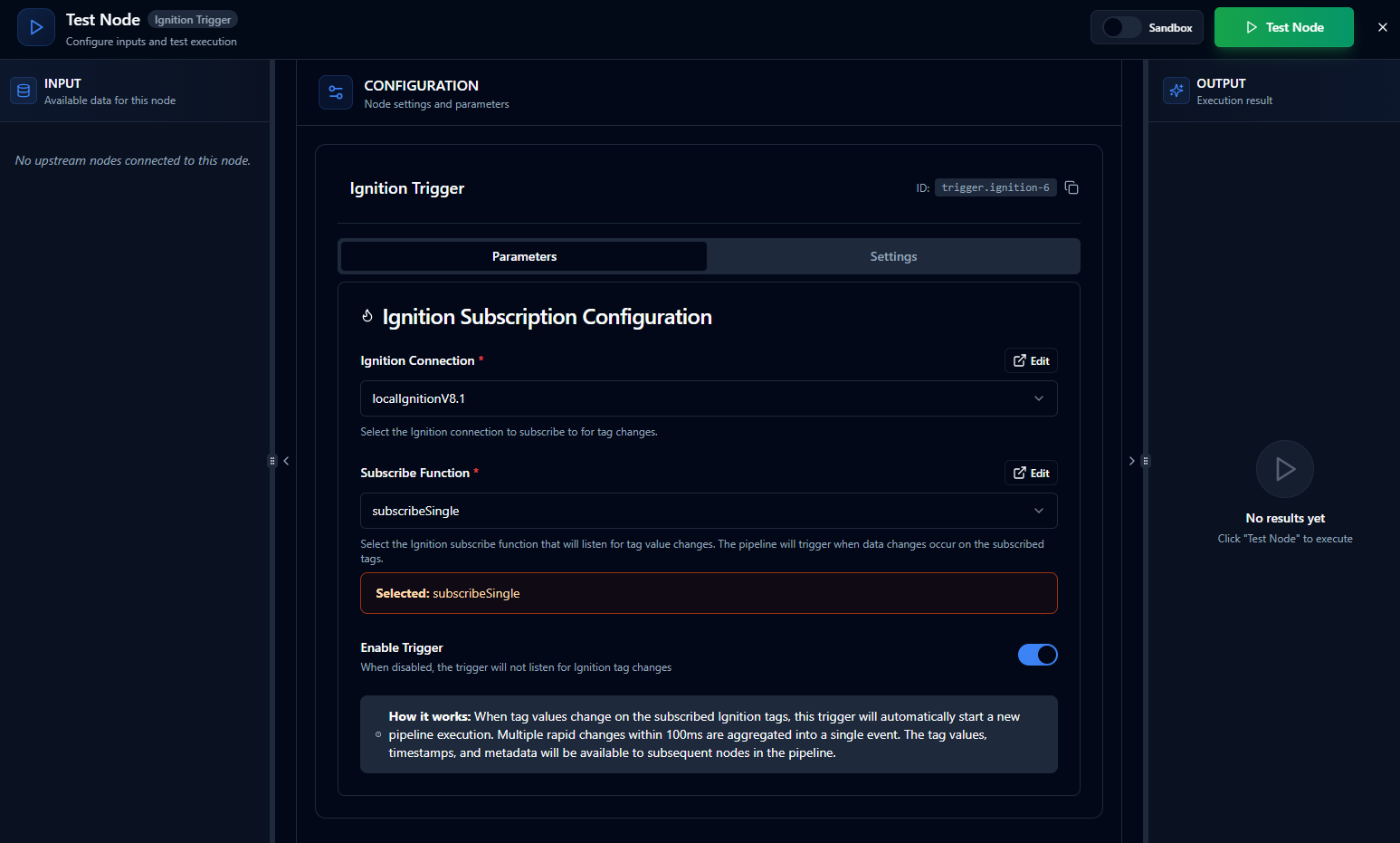
Parameters Configuration
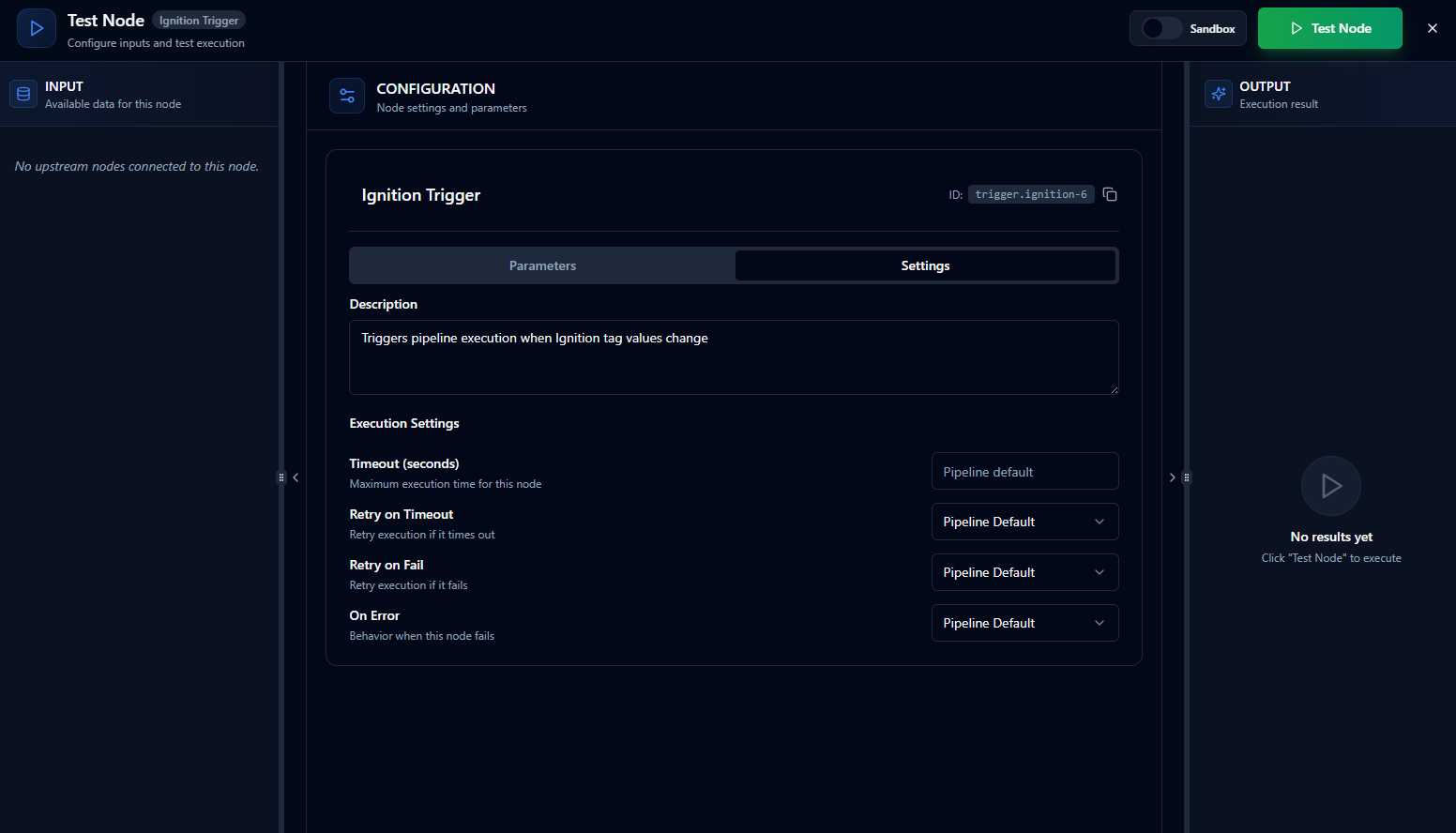
Settings Configuration
Basic Information
| Field | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Node Label | String (Required) | Display name for the node on the pipeline canvas |
| Description | String (Optional) | Explains what this trigger monitors and initiates |
Parameters
| Parameter | Type | Required | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Connection | Connection ID | Yes | - | The Ignition connection profile to use for subscribing |
| Function | Function ID | Yes | - | The Ignition Subscribe function that defines which tags to monitor |
| Enabled | Boolean | No | true | When disabled, the subscription is not created even if the pipeline is enabled |
The selected function must be an Ignition Subscribe function type. Read, write, or browse functions cannot be used with Ignition Trigger nodes.
Settings
Basic Settings
| Setting | Options | Default | Recommendation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Retry on Fail | true / false | false | Keep disabled for triggers—retries don't apply to event-driven nodes |
| Error Handling | Stop Pipeline / Continue | Stop Pipeline | Use "Stop Pipeline" to halt on critical failures |
Documentation Settings
| Setting | Type | Default | Purpose |
|---|---|---|---|
| Notes | Text | Empty | Document the trigger's purpose, monitored tags, or operational context |
| Display Note in Pipeline | Boolean | false | Show notes on the pipeline canvas for quick reference |
Output Data Structure
When Ignition tag changes trigger pipeline execution, the following data is available to downstream nodes via the $input variable.
Output Format
{
"type": "ignition_trigger",
"connectionId": "bf29be94-fc0a-4dc4-8e5c-092f1b74eb4b",
"functionId": "aef374c3-aa2b-454e-aabc-5657faac5950",
"enabled": true,
"node_id": "trigger.ignition-1",
"message": "Ignition trigger provides configuration for event-based triggering",
"values": [
{
"path": "[default]Line1/Temperature",
"value": 78.5,
"quality": "Good",
"timestamp": 1704067200000
},
{
"path": "[default]Line1/Pressure",
"value": 145.2,
"quality": "Good",
"timestamp": 1704067200050
}
]
}
Accessing Tag Data
In downstream nodes, use the $input variable to access the trigger output:
| Field | Expression | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Tag Values Array | $input.values | Array of all tag values that changed during the debounce window |
| Individual Tag | $input.values[0] | Access a specific tag by array index |
| Tag Path | $input.values[0].path | The full tag path including provider |
| Tag Value | $input.values[0].value | The current value of the tag |
| Tag Quality | $input.values[0].quality | Quality indicator (Good, Bad, Uncertain, etc.) |
| Tag Timestamp | $input.values[0].timestamp | Unix timestamp in milliseconds when the value changed |
| Connection ID | $input.connectionId | The Ignition connection profile used |
| Function ID | $input.functionId | The Subscribe function that received the changes |
| Node ID | $input.node_id | The trigger node identifier |
| Trigger Type | $input.type | Always ignition_trigger |
Use a JavaScript node or loop to iterate through $input.values and process each tag change:
$input.values.forEach(tag => {
if (tag.quality === 'Good') {
// Process good quality tag values
}
});
Validation Rules
The Ignition Trigger Node enforces these validation requirements:
Parameter Validation
Connection ID
- Must be provided and non-empty
- Must reference a valid Ignition connection profile
- Error: "Ignition connection is required"
Function ID
- Must be provided and non-empty
- Must reference a valid Ignition Subscribe function
- Function must belong to the specified connection
- Error: "Subscribe function is required"
Enabled Flag
- Must be a boolean if provided
- Error: "Enabled must be a boolean value"
Settings Validation
On Error
- Must be one of:
stopPipeline,continueExecution,retryNode - Error: "onError must be a valid error handling option"
Usage Examples
Production Line Monitoring
Scenario: Monitor critical process parameters on a production line and trigger alerts when values exceed thresholds.
Configuration:
- Label: Production Line Monitor
- Connection: Plant Floor Ignition Gateway
- Function: Subscribe to
[default]Line1/*(all tags on Line 1) - Enabled: true
Downstream Processing:
- Iterate through
$input.valuesarray - Check each tag value against configured thresholds
- Generate alerts for out-of-range values
- Log all changes to time-series database
- Update real-time dashboard
Equipment State Change Handler
Scenario: React to equipment state changes and coordinate downstream systems.
Configuration:
- Label: Equipment State Handler
- Connection: Manufacturing Ignition
- Function: Subscribe to
[default]Equipment/*/State(state tags for all equipment) - Enabled: true
Downstream Processing:
- Extract equipment ID from tag path
- Determine state transition (Running → Stopped, etc.)
- Update maintenance schedule if needed
- Notify operators of critical state changes
- Trigger dependent equipment adjustments
Alarm Acknowledgment Workflow
Scenario: Automatically process alarm acknowledgments and update external systems.
Configuration:
- Label: Alarm Ack Processor
- Connection: SCADA Ignition Gateway
- Function: Subscribe to
[default]Alarms/*/Acknowledged(acknowledgment status for all alarms) - Enabled: true
Downstream Processing:
- Filter for newly acknowledged alarms (value changed to true)
- Extract alarm details from tag path
- Log acknowledgment to audit database
- Send notification to maintenance system
- Update alarm dashboard
Multi-Tag Batch Processing
Scenario: Process related tag changes together for batch operations.
Configuration:
- Label: Batch Recipe Monitor
- Connection: Recipe Management Ignition
- Function: Subscribe to
[default]Recipe/Active/*(all active recipe parameters) - Enabled: true
Downstream Processing:
- Receive all recipe parameter changes in single event
- Validate complete recipe configuration
- Update PLC setpoints as a batch
- Log recipe change event
- Confirm successful application
Best Practices
Connection Health Monitoring
- Configure your Ignition connection with appropriate Keep Alive intervals
- Enable Auto Reconnect on the connection profile for automatic recovery
- Monitor connection status through MaestroHub's connection health dashboard
- Test reconnection behavior during maintenance windows
Designing Subscriptions
| Practice | Rationale |
|---|---|
| Group related tags | Leverage debouncing to process related changes together |
| Use specific tag paths | Reduces unnecessary processing and improves performance |
| Consider tag update rates | High-frequency tags may benefit from additional filtering |
| Monitor subscription count | Each subscription consumes gateway resources |
Working with Debounced Data
Processing the Values Array:
- Always check
$input.values.lengthbefore processing - Validate tag quality before using values
- Handle missing or null values gracefully
- Consider tag timestamps when ordering is important
Performance Considerations:
- The debounce window aggregates changes, reducing pipeline executions
- Process all tags in the array efficiently to maintain throughput
- Avoid heavy processing in tight loops over large tag arrays
Error Handling Strategies
For Critical Monitoring:
- Set On Error to
stopPipeline - Implement alerting for stopped pipelines
- Monitor pipeline execution failures
- Consider backup monitoring mechanisms
For Best-Effort Processing:
- Set On Error to
continueExecution - Log failed events for later analysis
- Ensure downstream nodes handle partial failures gracefully
- Implement retry logic for critical operations
Tag Quality Handling
Always check tag quality before processing values:
$input.values.forEach(tag => {
switch(tag.quality) {
case 'Good':
// Process reliable data
break;
case 'Bad':
// Log error, skip processing
break;
case 'Uncertain':
// Decide based on use case
break;
}
});
Enable vs. Disable
- Use the trigger's Enabled parameter to temporarily pause monitoring without changing pipeline state
- Disable triggers during maintenance windows to prevent unnecessary processing
- Document the reason for disabled triggers in the node's Notes field
- Re-enable triggers after testing configuration changes
Performance Optimization
| Scenario | Recommendation |
|---|---|
| High-frequency tags | Use specific subscriptions; consider additional filtering in Ignition |
| Large tag counts | Monitor pipeline execution queue; optimize downstream processing |
| Multiple triggers on same tags | MaestroHub optimizes with shared subscriptions—no action needed |
| Burst updates | Debouncing handles this automatically; ensure downstream can process arrays efficiently |
Troubleshooting
Common Issues
No Pipeline Executions
- Verify the trigger is enabled
- Check that the pipeline is enabled
- Confirm the Ignition connection is active
- Verify tags are actually changing values
- Check subscription function configuration
Missing Tag Changes
- Connection was down during changes (expected behavior)
- Tag quality may be Bad (filtered by subscription)
- Subscription function may not include the tag path
- Check Ignition Gateway subscription status
Too Many Pipeline Executions
- Debouncing should prevent this; verify 100ms window is working
- Check if multiple triggers are configured for same tags
- Review tag update rates in Ignition
Empty Values Array
- Subscription may have no matching tags
- All tag changes may have Bad quality
- Connection issue during debounce window