 Microsoft SQL Server Integration Guide
Microsoft SQL Server Integration Guide
Connect MaestroHub pipelines to Microsoft SQL Server instances for enterprise-grade data ingestion and orchestration. This guide highlights SQL Server specifics such as T-SQL, encryption policies, and authentication modes so you can configure pipelines with confidence.
Overview
The Microsoft SQL Server connector unlocks relational workloads with:
- Bidirectional data flows for reading and writing T-SQL queries
- Stored procedure execution with parameter binding and output handling
- Secure connectivity with TLS encryption and granular connection tuning
The connector is validated with Microsoft SQL Server 2012 and later.
Connection Configuration
Creating a Microsoft SQL Server Connection
Open Connections → New Connection → MSSQL and provide the following details:
MSSQL (Microsoft SQL Server) Connection Creation Fields
1. Profile Information
| Field | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Profile Name | - | A descriptive name for this connection profile (required, max 100 characters) |
| Description | - | Optional description for this MSSQL connection |
2. Database Configuration
| Field | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Host | localhost | Server hostname or IP address (required) |
| Port | 1433 | SQL Server port number (0-65535). Use 0 with instance name for auto-discovery via SQL Browser |
| Instance Name | - | Named instance (e.g., SQL2019, DEV, SQLEXPRESS). Leave empty for default instance (MSSQLSERVER) |
| Database | - | Initial database name to connect to (required, e.g., master) |
| Connect Timeout (sec) | 30 | Connection timeout in seconds (0-600) - required |
- Supported SQL Server Versions: 2012 and newer
- Instance Name: Used for named instances. If using default instance (MSSQLSERVER), leave empty
- Port 0: When port is set to 0, SQL Browser service will be used to discover the port based on instance name
3. Basic Authentication
| Field | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Username | - | SQL Server database username (required, e.g., sa) |
| Password | - | SQL Server user password (required) |
4. Encryption Settings
4a. Encryption Configuration
| Field | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Encryption Mode | disable | Connection encryption level (disable / true / strict) |
| Trust Server Certificate | true | Accept self-signed or untrusted certificates. Enable for development, disable for production with valid CA certificates |
Encryption Mode Options
- disable: No encryption - Data transmitted in plain text
- true: TLS encryption enabled - Secure connection with TLS
- strict: Mandatory TLS (SQL Server 2022+ only) - Enforces strict TLS encryption
4b. Certificate Verification
(Only displayed when Encryption Mode is NOT "disable" AND Trust Server Certificate is disabled)
| Field | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
| CA Certificate | - | CA certificate for server verification (PEM format). Only required for self-signed or private CA certificates. Leave empty if using public CAs (Let's Encrypt, DigiCert, etc.) |
5. Connection Pool Settings
| Field | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Max Open Connections | 100 | Maximum number of simultaneous database connections (1-1000). Higher values increase concurrency but add DB load |
| Max Idle Connections | 25 | Idle connections kept ready for reuse to reduce latency (0-1000). Set 0 to close idle connections immediately |
| Connection Max Lifetime (sec) | 900 | Maximum age of a connection before it is recycled (0-86400 sec, 0 = keep indefinitely) |
| Connection Max Idle Time (sec) | 300 | How long an idle connection may remain unused before being closed (0-86400 sec, 0 = disable idle timeout) |
Connection Pool Best Practices
- Max Open Connections: Balance between concurrency and database load. Default 100 is suitable for most applications
- Max Idle Connections: Keeping idle connections reduces connection establishment latency
- Max Lifetime: Prevents connection leaks and helps with database maintenance windows (default 900 sec = 15 minutes)
- Max Idle Time: Closes unused connections to free up database resources (default 300 sec = 5 minutes)
6. Retry Configuration
| Field | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Retries | 3 | Number of connection retry attempts (0-10). 0 means no retry |
| Retry Delay (ms) | 200 | Initial delay between retry attempts in milliseconds (0-3,600,000 ms = 1 hour max) |
| Retry Backoff Multiplier | 2 | Exponential factor for retry delay growth (1.0-10.0, e.g., 2 means delay doubles each retry) |
Retry Behavior Example
- 1st retry: wait 200ms
- 2nd retry: wait 400ms (200 × 2)
- 3rd retry: wait 800ms (400 × 2)
7. Connection Labels
| Field | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Labels | - | Key-value pairs to categorize and organize this MSSQL connection (max 10 labels) |
Example Labels
env: prod- Environment (production, staging, development)team: data- Responsible teamregion: us-east- Geographical regionapplication: erp- Associated application
- SQL Server Version Support: This connector supports Microsoft SQL Server 2012 and newer versions
- Named Instances: SQL Server supports multiple instances on the same server. Use Instance Name for non-default instances
- Encryption Recommendations: Development: Use encrypt: disable or trustServerCertificate: true for convenience. Production: Use encrypt: true or encrypt: strict with trustServerCertificate: false and valid CA certificates
- Connection Pooling: The driver uses Go's database/sql connection pool, which efficiently manages connections
- Retry Strategy: Implements exponential backoff for connection failures to handle transient network issues
- Fields marked as required must be filled out before creating/saving the connection
- All timeout values are in seconds unless otherwise specified (Retry Delay is in milliseconds)
Function Builder
Creating MSSQL Functions
After the connection is saved, create reusable SQL Server functions:
- Navigate to Functions → New Function
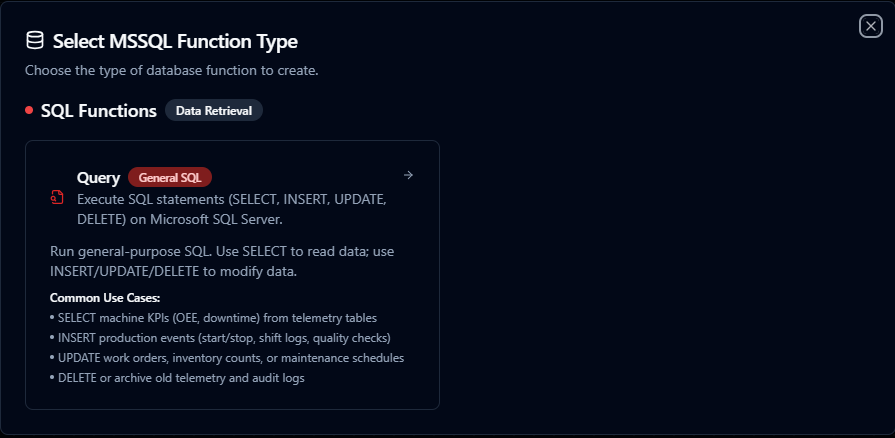
- Choose Query as the function type
- Select the SQL Server connection you configured
- Compose your T-SQL statement with parameter placeholders
MSSQL query function editor with T-SQL and parameter binding
Query Function
Purpose: Execute SQL statements (SELECT, INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE) on Microsoft SQL Server. Run general-purpose SQL to read or modify data in your SQL Server database.
Configuration Fields
| Field | Type | Required | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SQL Query | String | Yes | - | SQL statement to execute (SELECT or INSERT/UPDATE/DELETE). Supports parameterized queries. |
| Timeout (seconds) | Number | No | 0 | Per-execution timeout in seconds. Sets maximum time allowed for query execution. |
Use Cases:
- SELECT machine KPIs (OEE, downtime) from telemetry tables
- INSERT production events (start/stop, shift logs, quality checks)
- UPDATE work orders, inventory counts, or maintenance schedules
- DELETE or archive old telemetry and audit logs
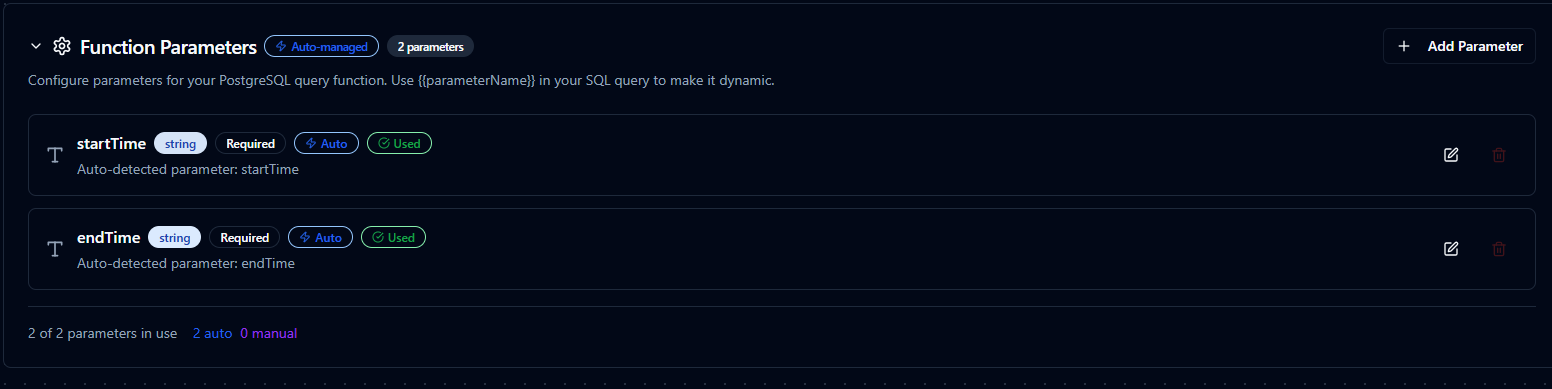
Using Parameters
MaestroHub detects the ((parameterName)) syntax and exposes each parameter for validation and runtime binding.
| Configuration | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Type | Enforce data types for incoming values | string, number, boolean, datetime, array |
| Required | Mark parameters as mandatory or optional | Required / Optional |
| Default Value | Fallback value applied when callers omit a parameter | SYSDATETIMEOFFSET(), 0, 'Active' |
| Description | Add guidance for downstream users | "UTC start time for the query window" |
Parameter configuration with validation rules and helper text
Pipeline Integration
Use the Microsoft SQL Server query functions you publish here as nodes inside the Pipeline Designer to keep plant-floor activity aligned with enterprise data. Drag the query node into your flow, bind parameters to upstream outputs or constants, and adjust error handling or retry behavior directly on the canvas.
When orchestrating larger workflows, visit the Connector Nodes page for guidance on where SQL Server nodes fit within multi-system automation patterns.
SQL Server query node with connection, function, and parameter bindings
Common Use Cases
Hourly Production Metrics
Scenario: Build hourly OEE dashboards pulling data from MES tables.
WITH Hourly AS (
SELECT
DATEADD(hour, DATEDIFF(hour, 0, event_time), 0) AS hour_bucket,
line_id,
SUM(runtime_minutes) AS runtime_minutes,
SUM(planned_minutes) AS planned_minutes,
SUM(good_units) AS good_units,
SUM(reject_units) AS reject_units
FROM dbo.OEEEvents
WHERE event_time BETWEEN ((startTime)) AND ((endTime))
GROUP BY DATEADD(hour, DATEDIFF(hour, 0, event_time), 0), line_id
)
SELECT
hour_bucket,
line_id,
CAST((good_units * 1.0) / NULLIF(good_units + reject_units, 0) * 100 AS DECIMAL(5,2)) AS quality_pct,
CAST(runtime_minutes / NULLIF(planned_minutes, 0) * 100 AS DECIMAL(5,2)) AS availability_pct
FROM Hourly
ORDER BY hour_bucket DESC, line_id;
Pipeline Integration: Populate BI datasets, KPI dashboards, or notify teams when efficiency dips.
Writing Work Order Progress
Scenario: Update work order completion details from barcode scanners or PLC events.
UPDATE dbo.WorkOrders
SET
completed_quantity = ((completedQuantity)),
scrap_quantity = ((scrapQuantity)),
status = ((newStatus)),
last_updated_at = SYSDATETIME(),
last_updated_by = ((userId))
WHERE work_order_id = ((workOrderId))
OUTPUT inserted.work_order_id, inserted.status, inserted.completed_quantity;
Pipeline Integration: Trigger on event streams to keep ERP and MES systems synchronized in real time.
Inventory Synchronization
Scenario: Mirror warehouse movements from automation equipment into ERP tables.
MERGE dbo.InventoryBalances AS target
USING (VALUES
((itemNumber)),
((locationCode)),
((quantityDelta)),
((transactionId))
) AS source(item_number, location_code, quantity_delta, transaction_id)
ON target.item_number = source.item_number
AND target.location_code = source.location_code
WHEN MATCHED THEN
UPDATE SET
quantity_on_hand = quantity_on_hand + source.quantity_delta,
last_transaction_id = source.transaction_id,
updated_at = SYSDATETIME()
WHEN NOT MATCHED THEN
INSERT (item_number, location_code, quantity_on_hand, last_transaction_id, updated_at)
VALUES (source.item_number, source.location_code, source.quantity_delta, source.transaction_id, SYSDATETIME());
Pipeline Integration: Combine with Modbus, OPC UA, or REST nodes to maintain accurate inventory balances.
Data Archiving and Cleanup
Scenario: Offload historical sensor data into archive tables to maintain performance.
WITH Archived AS (
DELETE TOP (10000) FROM dbo.SensorReadings
OUTPUT deleted.*
WHERE reading_time < DATEADD(day, -((retentionDays)), SYSUTCDATETIME())
)
INSERT INTO dbo.SensorReadingsArchive (
sensor_id,
reading_time,
temperature,
pressure,
vibration,
archived_at
)
SELECT
sensor_id,
reading_time,
temperature,
pressure,
vibration,
SYSUTCDATETIME()
FROM Archived;
Pipeline Integration: Schedule via cron triggers to run during maintenance windows or low-traffic periods.