 Siemens S7 Integration Guide
Siemens S7 Integration Guide
MaestroHub integrates natively with Siemens S7 PLC families. Author reusable functions for deterministic reads and writes, manage security, and orchestrate PLC communication inside your pipelines.
Overview
The Siemens S7 connector provides:
- Direct communication over the S7 protocol through Maestro Agents or secure network tunnels
- Structured data access for Data Blocks, Inputs, Outputs, Markers, Timers, and Counters
- Type-aware conversions for BOOL, INT, DINT, REAL, STRING, and custom structures
- Session management with configurable rack/slot addressing and connection diagnostics
Connection Configuration
Creating a Siemens S7 Connection
Navigate to Connections → New Connection → Siemens S7 and configure the PLC endpoint with the following fields.
Siemens S7 Connection Creation Fields
1. Profile Information
| Field | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Profile Name | - | A descriptive name for this connection profile (required, max 100 characters) |
| Description | - | Optional description for this S7 connection |
2. S7 Connection Settings
| Field | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
| PLC Address | 192.168.1.100:102 | PLC IP address and port (format: host:port) – required, port must be 1-65535 |
| Rack | 0 | PLC rack number (0-7) – required |
| Slot | 1 | PLC slot number (0-31) – required |
| Connection Type | Programming Device (PG) | S7 connection mode – required |
Connection Type Options
| Connection Type | Value | Description | Typical Use Cases |
|---|---|---|---|
| Programming Device (PG) | 1 | For programming and diagnostics | PLC programming and diagnostics System monitoring and debugging Configuration and maintenance |
| Operator Panel (OP) | 2 | For operator panels and HMI | HMI and operator interfaces Data visualization panels Process monitoring applications |
| Basic Connection | 3 | Basic data exchange | Simple data exchange Basic communication needs Limited access scenarios |
3. Timeout Configuration
| Field | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Request Timeout (ms) | 10000 | Maximum time to wait for S7 response (0-300000 ms, 0-5 minutes) |
| Idle Timeout (ms) | 30000 | Close connection after idle period (0-1800000 ms, 0-30 minutes, 0 = never) |
| Retry Count | 2 | Number of retries on communication failure (0-10) |
| Retry Delay (ms) | 1000 | Delay between retry attempts (0-60000 ms, 0-60 seconds) |
4. Security Configuration
| Field | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Session Password | - | Optional password for protected PLCs (max 8 characters) |
5. Connection Labels
| Field | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Labels | - | Key-value pairs to categorize and organize this S7 connection (max 10 labels) |
Example Labels
environment: production– Deployment environmentline: line-1– Production lineplc-type: s7-1200– PLC modellocation: factory-floor– Physical location
- Standard Port: The default S7 communication port is 102 (ISO-on-TCP).
- Rack and Slot: These values identify the CPU module location in the PLC rack (common combinations: rack = 0 with slot 1 or slot 2). Check your PLC hardware configuration for exact values.
- Connection Type Selection: PG provides full access for development/diagnostics, OP is tailored for HMIs, and Basic is for minimal data exchange.
- Password Protection: Only required if the PLC has password protection enabled in its security settings.
- Timeout Recommendations: Use a 10000 ms request timeout for local networks (increase for remote) and set idle timeout to 30000 ms or higher depending on application needs.
- Address Format: Must be
host:port. Host can be an IP address or hostname and port must be 1-65535 (102 is typical for S7). - Security Note: Session passwords are stored securely and used for establishing authenticated connections to protected PLCs.
Function Builder
Creating Siemens S7 Functions
Once the connection is saved:
- Go to Functions → New Function
- Choose S7 Read or S7 Write
- Select the Siemens S7 connection profile
- Define addresses, data types, and optional scaling/structure metadata
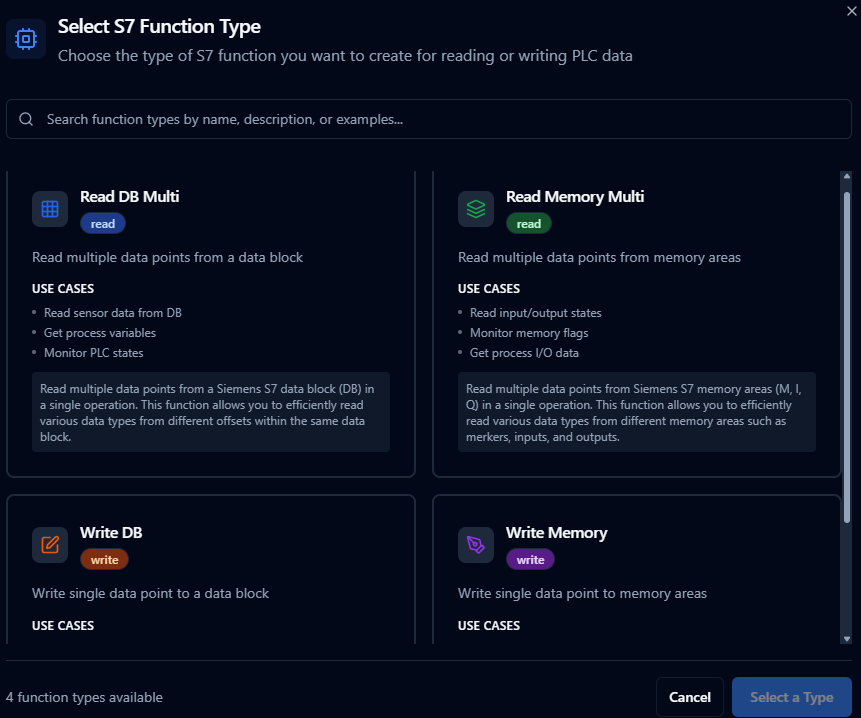
Author Siemens S7 read/write functions with address templates and data type mapping
Quick Add: Bulk Function Creation
For situations requiring multiple S7 functions to be created efficiently, the Quick Add feature enables batch creation through an interactive table or CSV import.
When to Use Quick Add
- Commissioning a new S7 PLC with numerous data blocks and memory areas
- Migrating tag databases from TIA Portal or other engineering tools
- Setting up standardized data acquisition across multiple PLCs
- Quickly establishing connectivity for testing and validation
How to Use Quick Add
- Navigate to your Siemens S7 connection in Connections
- Click Quick Add Functions button
- Choose your input method:
- Table Entry: Add function definitions row by row
- CSV Import: Upload a CSV file with PLC addresses and data types
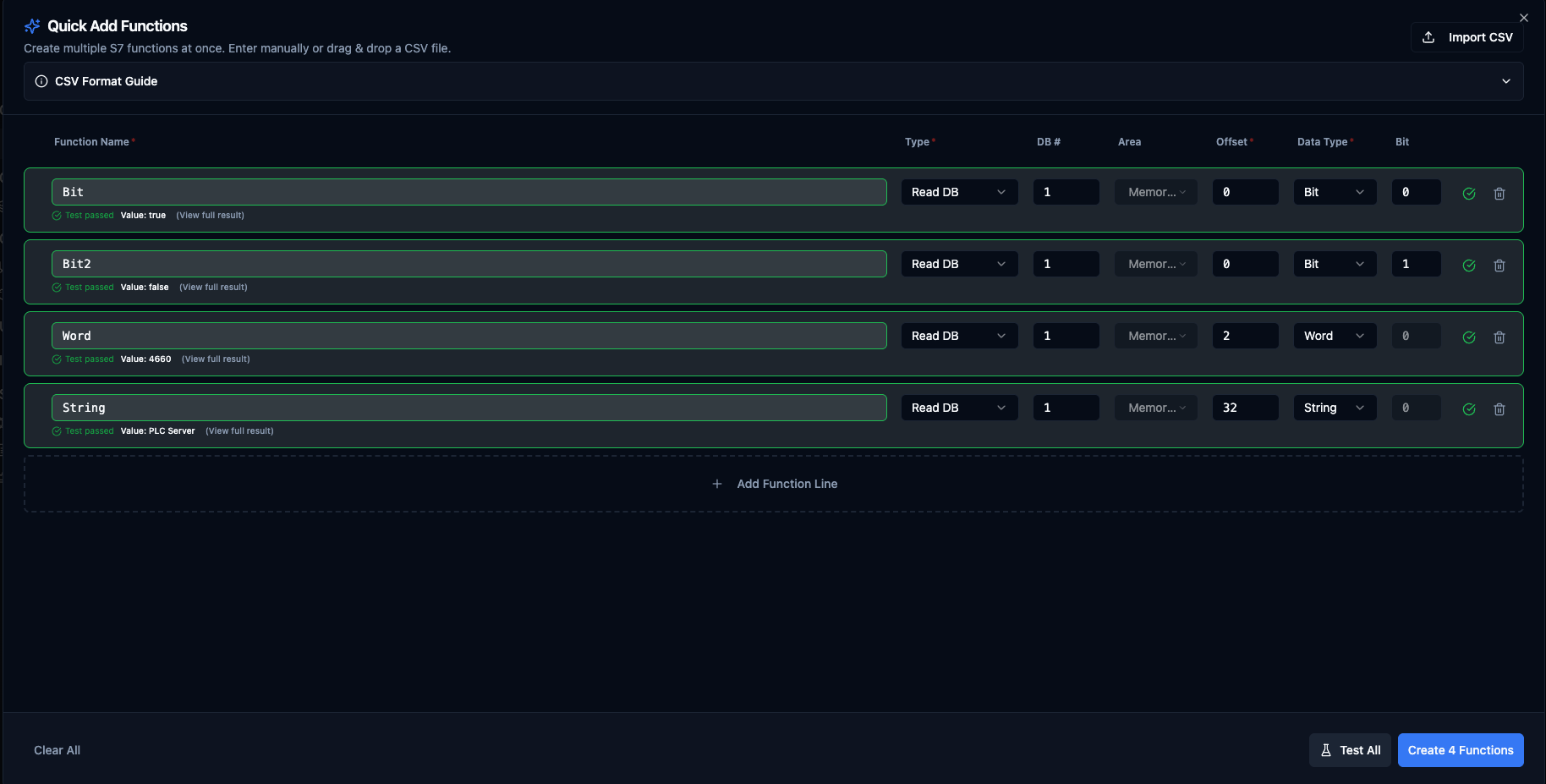
Quick Add Functions dialog for Siemens S7 with table entry and CSV import options
Table Columns
| Column | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Function Name | Unique identifier for the function | DB100_MotorSpeed |
| Type | S7 operation type | Read DB, Write DB, Read Memory, Write Memory |
| DB # | Data block number (DB operations only) | 100 |
| Area | Memory area (Memory operations only) | I (Input), Q (Output), M (Memory) |
| Offset | Byte offset within DB or memory area | 10 |
| Data Type | S7 data type | REAL, INT, DINT, BIT, STRING |
| Bit | Bit position (BIT data type only) | 0-7 |
Supported Function Types
- Read DB: Read from Data Block (multi-point read)
- Write DB: Write to Data Block (single-point write)
- Read Memory: Read from memory areas I, Q, M (multi-point read)
- Write Memory: Write to memory areas Q, M (single-point write)
Data Type Options
- BIT: Single bit (requires bit position 0-7)
- BYTE: 8-bit unsigned (1 byte)
- WORD: 16-bit unsigned (2 bytes)
- DWORD: 32-bit unsigned (4 bytes)
- CHAR: Single character (1 byte)
- STRING: Text string (256 bytes)
- INT: 16-bit signed integer (2 bytes)
- DINT: 32-bit signed integer (4 bytes)
- REAL: 32-bit floating point (4 bytes)
- LREAL: 64-bit floating point (8 bytes)
Memory Area Options
- I: Process Inputs (read only)
- Q: Process Outputs (read/write)
- M: Memory (Merkers) (read/write)
CSV Import Format
name,functionType,dbNumber,area,start,dataType,bitPos
MotorTemp,s7.read.db.multi,1,,10,REAL,
PumpStatus,s7.read.db.multi,1,,14,BIT,0
InputSignal,s7.read.memory.multi,,I,0,WORD,
OutputControl,s7.write.memory,,Q,20,BIT,3
Validation Rules
- Function names must be unique within the connection
- DB operations: DB number is required (must be ≥ 0)
- Memory operations: Memory area (I/Q/M) is required
- Offset is always required (byte position within DB or memory area)
- BIT data type: Bit position (0-7) is required
- Write operations to Process Inputs (I) are not permitted
Best Practices
- Use structured naming conventions that reflect the PLC program structure (e.g.,
DB100_Zone1_Temp) - Group related data points by data block number or memory area
- Validate bit positions carefully when working with BIT data types
- For DB operations, document which data block corresponds to which equipment or process
- Test with a small sample before bulk importing hundreds of functions
- Keep CSV files organized by PLC or production line for easy maintenance
Read DB Multi Function
Purpose: Read multiple data points from a Siemens S7 data block (DB) in a single operation. Allows efficient reading of various data types from different offsets within the same data block.
Configuration Fields
| Field | Type | Required | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Data Block Number | Number | Yes | 1 | The DB number to read from (e.g., DB100). Minimum: 0 |
| Data Points | Array | Yes | See below | List of data points to read from the data block (minimum 1 point) |
Data Point Fields:
| Field | Type | Required | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Point Name | String | Yes | point1 | Unique name for this data point (1-100 characters) |
| Start Offset | Number | Yes | 0 | Byte offset within the data block (0-65535) |
| Size (bytes) | Number | Yes | 4 | Number of bytes to read (1-65536) |
| Data Type | String | Yes | REAL | S7 data type: BIT, BYTE, WORD, DWORD, CHAR, STRING, WSTRING, INT, DINT, REAL, LREAL, TIMER, TIME_OF_DAY, DATE_AND_TIME, COUNTER |
Use Cases: Read sensor data from DB, get process variables, monitor PLC states, bulk data acquisition
Read Memory Multi Function
Purpose: Read multiple data points from Siemens S7 memory areas (M, I, Q) in a single operation. Allows efficient reading of various data types from different memory areas such as merkers, inputs, and outputs.
Configuration Fields
| Field | Type | Required | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Memory Area | String | Yes | M | S7 memory area to read from: M (Merkers), I (Process Inputs), Q (Process Outputs) |
| Data Points | Array | Yes | See below | List of data points to read from the memory area (minimum 1 point) |
Data Point Fields:
| Field | Type | Required | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Point Name | String | Yes | point1 | Unique name for this data point (1-100 characters) |
| Start Address | Number | Yes | 0 | Memory address/offset (0-65535) |
| Size (bytes) | Number | Yes | 1 | Number of bytes to read (1-65536) |
| Data Type | String | Yes | BIT | S7 data type: BIT, BYTE, WORD, DWORD, CHAR, STRING, WSTRING, INT, DINT, REAL, LREAL, TIMER, TIME_OF_DAY, DATE_AND_TIME, COUNTER |
Use Cases: Read input/output states, monitor memory flags, get process I/O data, system status monitoring
Write DB Function
Purpose: Write a single data point to a Siemens S7 data block (DB). Allows writing various data types to specific offsets within a data block for control and configuration operations.
Configuration Fields
| Field | Type | Required | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Data Block Number | Number | Yes | 1 | The DB number to write to (e.g., DB100). Minimum: 0 |
| Start Offset | Number | Yes | 0 | Byte offset within the data block (0-65535) |
| Bit Position | Number | No | 0 | Bit position (0-7, only required for BIT data type) |
| Size (bytes) | Number | No | 4 | Number of bytes (auto-calculated based on data type) (1-65536) |
| Data Type | String | Yes | REAL | S7 data type: BIT, BYTE, WORD, DWORD, CHAR, STRING, WSTRING, INT, DINT, REAL, LREAL, TIMER, TIME_OF_DAY, DATE_AND_TIME, COUNTER |
| Value | String | Yes | - | Value to write (format depends on data type). Examples: true (BIT), 255 (BYTE), 25.5 (REAL), Hello (STRING) |
Use Cases: Set configuration values, update setpoints, write control commands, configuration management
Write Memory Function
Purpose: Write a single data point to Siemens S7 memory areas (M, Q). Allows writing various data types to different memory areas for control and status operations. Note: Process Inputs (I) are read-only.
Configuration Fields
| Field | Type | Required | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Memory Area | String | Yes | M | S7 memory area to write to: M (Merkers), Q (Process Outputs). Note: Process Inputs (I) are read-only |
| Start Address | Number | Yes | 0 | Memory address/offset (0-65535) |
| Bit Position | Number | No | 0 | Bit position (0-7, only required for BIT data type) |
| Size (bytes) | Number | No | 1 | Number of bytes (auto-calculated based on data type) (1-65536) |
| Data Type | String | Yes | BIT | S7 data type: BIT, BYTE, WORD, DWORD, CHAR, STRING, WSTRING, INT, DINT, REAL, LREAL, TIMER, TIME_OF_DAY, DATE_AND_TIME, COUNTER |
| Value | String | Yes | - | Value to write (format depends on data type). Examples: true (BIT), 255 (BYTE), 25.5 (REAL), Hello (STRING) |
Use Cases: Set output states, write memory flags, control I/O operations, system control commands
Using Parameters
Enclose dynamic values within ((parameterName)) to expose them for validation and runtime binding.
| Configuration | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Type | Ensure proper coercion | number, boolean, string, datetime |
| Required | Mark critical parameters | Required / Optional |
| Default Value | Provide safe baseline values | 20.0, false |
| Description | Document usage for collaborators | "Mixing temperature in °C", "Enable discharge gate" |
Parameter validation, defaults, and helper text for Siemens S7 functions
Pipeline Integration
Use the Siemens S7 connection functions you configure here as nodes inside the Pipeline Designer to coordinate PLC reads and writes with downstream logic. Drag in the read or write node, bind parameters to upstream outputs or constants, and fine-tune retries or operator guidance without leaving the canvas.
For orchestration blueprints that combine S7 with analytics, SQL, or notification steps, review the Connector Nodes page to understand how these nodes fit into broader automation strategies.
S7 node with connection binding and parameter configuration
Common Use Cases
Production Data Acquisition
Poll Data Blocks for production counts, cycle times, and recipe parameters, then push results to historians or ERP systems.
Supervisory Control
Deliver validated setpoints or mode changes to the PLC in response to business logic, alarms, or operator approvals.
Maintenance Diagnostics
Expose diagnostic bits, buffer alarms, or timer states to maintenance dashboards for rapid troubleshooting.