Convert to File node
Convert to File Node
Overview
- Type:
transform.data.serializer - Display Name: Convert to File
- Category: transform
- Execution:
supportsExecution: true - I/O Handles:
- Input:
defaultIn(left), label: Input - Outputs:
result(Success),error(Error)
- Input:
Purpose: Serializes structured input into CSV or Excel payloads. Supports header control, flexible input mapping, boolean/null formatting, and output encoding for safe transport to file writers or connectors.
Configuration Reference
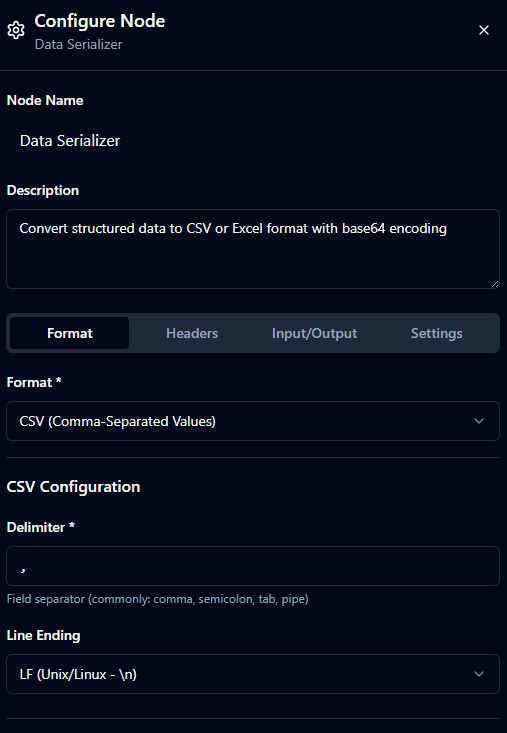
Format
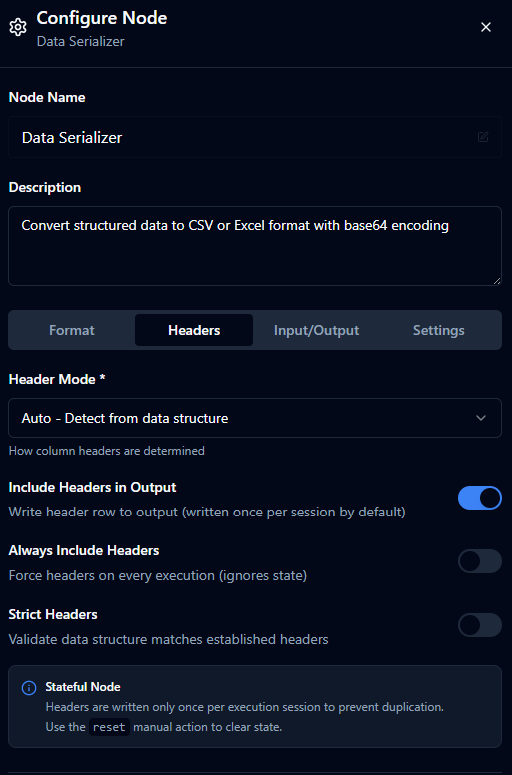
Headers
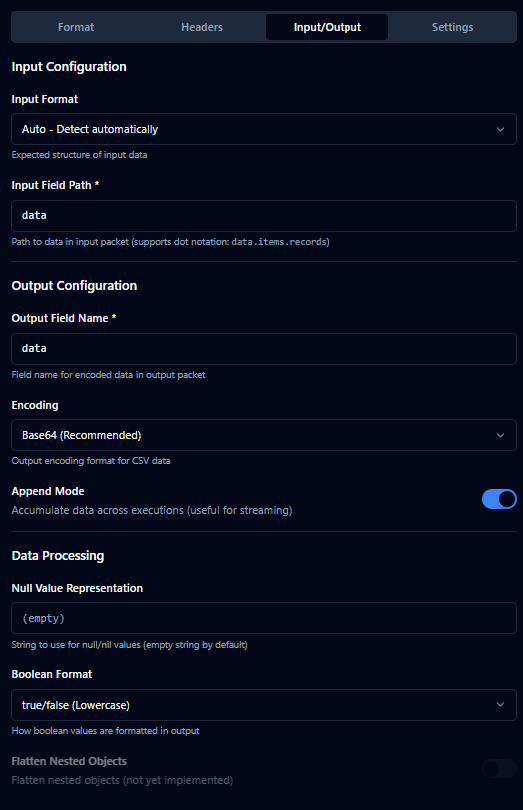
Input / Output
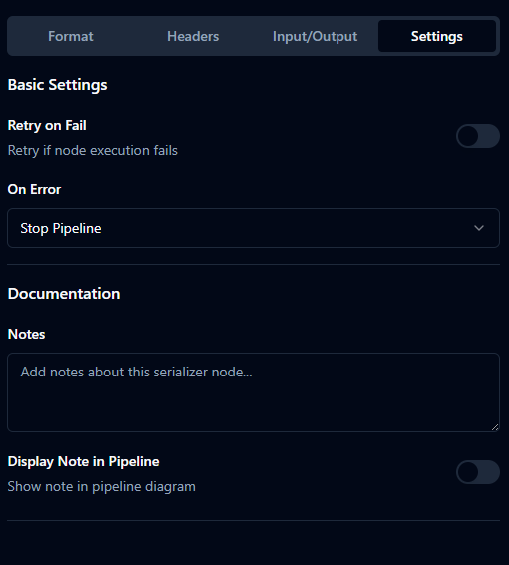
Settings
Format
| Field | Type | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Format | enum | csv | Output file format: csv or excel. |
| Delimiter (CSV) | string | , | Field separator (comma, semicolon, tab, pipe). Must not be empty. |
| Line Ending (CSV) | enum | LF | Line terminator style: LF or CRLF. |
| Sheet Name (Excel) | string | Sheet1 | Required. Max 31 chars. Cannot include / \\ ? * [ ]. |
| Auto Filter (Excel) | boolean | true | Adds auto-filter to header row. |
| Freeze Header (Excel) | boolean | true | Freeze panes at header row. |
Headers
| Field | Type | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Header Mode | enum | auto | How to determine headers: auto, provided, fromFirstRow, or none. |
| Headers | string[] | [] | Required when headerMode === 'provided'. Ordered list of header names. |
| Include Headers | boolean | true | Writes header row. |
| Always Include Headers | boolean | false | When includeHeaders, forces header row every execution (useful for Excel overwrite). |
| Strict Headers | boolean | false | Validates data structure against established headers. |
Stateful header behavior
Headers are written once per execution session. Use the node's reset manual action to clear state and force a new header write when needed.
Input / Output
| Field | Type | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Input Format | enum | auto | Expected structure: auto, arrayOfArrays, or arrayOfObjects. |
| First Row Is Header | boolean | false | When inputFormat === 'arrayOfArrays', treat first row as headers. |
| Input Field | string | data | Dot path to the data to serialize (e.g., data.items.records). |
| Output Field | string | data | Where the encoded payload is placed in the output packet. |
| Encoding | enum | base64 | base64 or utf8. Excel is always base64 (binary); CSV supports both. |
| Append Mode | boolean | true | Accumulate data across executions (useful for streaming). |
Data Processing
| Field | Type | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Null Value | string | "" | Text used for null values. |
| Boolean Format | enum | true/false | Boolean string format: true/false, TRUE/FALSE, or 1/0. |
| Flatten Nested | boolean | false | Reserved for future use; flattens nested objects when enabled. |
Settings
| Field | Type | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Retry on Fail | boolean | false | Retry on transient errors. |
| On Error | enum | stopPipeline | One of: stopPipeline, continueExecution, retryNode. |
| Notes | string | "" | Documentation notes for collaborators. |
| Display Note in Pipeline | boolean | false | Show notes on the pipeline canvas. |
Validation Rules
- Node label: required (non-empty)
- format: required; must be
csvorexcel - CSV: delimiter required and non-empty
- Excel: sheetName required; must not contain
/ \\ ? * [ ] - headerMode: must be one of
auto|provided|fromFirstRow|none - When
headerMode === 'provided':headersmust be a non-empty array - inputField: required (non-empty)
- outputField: required (non-empty)
Typical Integration
- Upstream: Use parsing/processing nodes (e.g., CSV/Excel Processor) to produce structured data (
arrayOfObjectspreferred;arrayOfArrayssupported). - Downstream:
- For file output, wire into a file write function (e.g., Local File connector “Write” function).
- When Local File “Fetch” is used earlier, the typical flow is: Fetch raw file → process → serialize → write file.
Examples
-
CSV output for a
.csvfile:format: 'csv'delimiter: ',',lineEnding: 'LF'headerMode: 'auto',includeHeaders: trueinputFormat: 'arrayOfObjects'inputField: 'data.records',outputField: 'data'encoding: 'base64'(recommended for binary-safe transport)appendMode: falsefor one-shot exports
-
Excel output for an
.xlsxfile:format: 'excel'sheetName: 'Summary',autoFilter: true,freezeHeader: trueheaderMode: 'auto',includeHeaders: true,alwaysIncludeHeaders: true(useful for overwrite flows)inputFormat: 'arrayOfObjects'inputField: 'data.items',outputField: 'data'encoding: 'base64'(fixed for Excel)
Recommended Usage with Local File Functions
-
Serialize → Write to file:
- Connect Serializer
result→ Local Filewritefunction node. - Set Local File
functionConfig.datato the serializer’soutputField(defaultdata). - For CSV: choose
encodingper downstream; for Excel: base64 is automatic.
- Connect Serializer
-
Using Local File Fetch upstream:
- If Fetch is used to read source data, ensure processors convert it into the structure expected by Serializer:
arrayOfObjects(preferred), orarrayOfArrays(enablefirstRowIsHeaderif first row holds headers).
- If Fetch is used to read source data, ensure processors convert it into the structure expected by Serializer: