Smart Connector Node
Smart Connector Node
Overview
The Smart Connector Node is a dynamic connector that decides which connection and which function to use at runtime based on pipeline data.
Instead of hard-coding a single connection profile and function in the node configuration, you provide expressions that resolve to the right connection and function for each execution, with optional caching for high performance.
This makes Smart Connector ideal for:
- Multi-tenant routing where each tenant has its own connection profile.
- Conditional system selection (premium vs. standard processors).
- Dynamic protocol or data-source selection (PLC vs. MQTT vs. REST) using a single node.
Configuration Reference
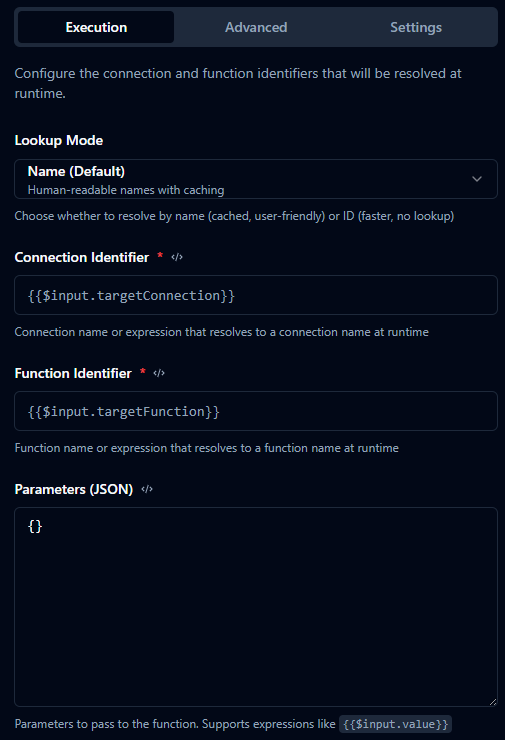
Execution Tab
Advanced Tab
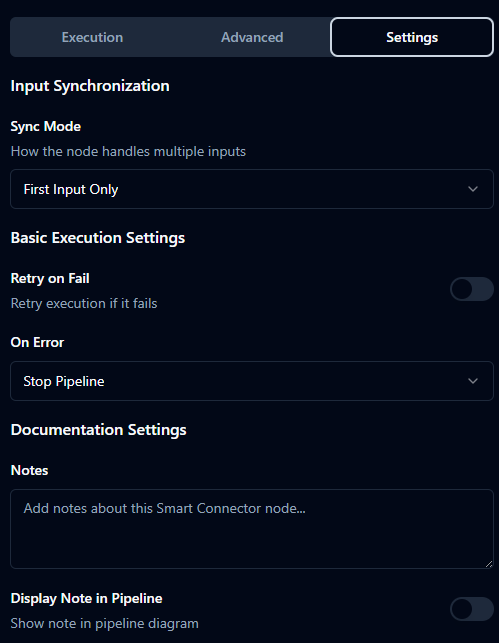
Settings Tab
Execution Tab
| Field | Type | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Lookup Mode | string | "name" | How identifiers are resolved: "name" (cached name→ID) or "id" (direct UUID). |
| Connection Identifier | string | "" | Expression resolving to a connection name or ID. Required. |
| Function Identifier | string | "" | Expression resolving to a function name or ID. Required. |
| Parameters | object | {} | Key/value map passed to the function. Each value may be a literal or expression. |
Advanced Tab
| Field | Type | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Timeout Override | number | empty | Optional timeout (seconds) overriding the function’s default timeout. |
| Debug Mode | boolean | false | Enables detailed logging and additional metrics. |
| Cache TTL | number | 300 (name mode) | Cache time-to-live in seconds for name lookups. 0 disables caching. |
Expression Examples
- Connection identifier:
{{$input.targetConnection}}{{$input.tenantId}}-database
- Function identifier:
{{$input.targetFunction}}{{$input.amount > 10000 ? "process-premium" : "process-standard"}}
- Parameters object (JSON editor):
{
"orderId": "{{$input.orderId}}",
"amount": "{{$input.amount}}",
"currency": "{{$input.currency || 'USD'}}"
}
Settings Tab
| Field | Type | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Retry on Fail | boolean | false | Automatically retry transient failures from the connection function. |
| On Error | string | "stopPipeline" | Error strategy: stop the pipeline or continue via error branch depending on your UI options. |
| Notes | string | "" | Internal documentation about routing logic and usage. |
| Display Note in Pipeline | boolean | false | Shows notes on the canvas near the node. |
| Input Sync Mode | string | "first" | When multiple upstream inputs feed this node, "first" executes as soon as one packet arrives. |
| Wait Timeout | string | "30s" | Max time to wait when sync modes are changed (for advanced scenarios). |
Usage Examples
Single Pipeline for Multiple Connections (For-Each + Smart Connector)
In many production scenarios you maintain a list of connections and functions (for different lines, machines, or tenants). Instead of adding many static connector nodes to the pipeline, you can:
- Use a For-Each Loop node that iterates over the list.
- Place one Smart Connector node inside the loop.
- Let Smart Connector resolve the correct connection and function for each item at runtime.
Assume the incoming payload to the For-Each Loop looks like:
{
"connections": [
{ "connectionName": "line-1-plc", "functionName": "target-function", "payload": { "line": 1 } },
{ "connectionName": "line-2-plc", "functionName": "target-function", "payload": { "line": 2 } }
]
}
Configure the For-Each Loop to iterate over connections, so the Smart Connector receives each item as $input.
| Field | Value |
|---|---|
| Lookup Mode | name |
| Connection Identifier | {{$input.connectionName}} |
| Function Identifier | {{$input.functionName}} |
| Parameters | {{$input.payload}} |
With this pattern:
- You keep a single pipeline definition instead of duplicating many connector nodes.
- Adding a new connection is as simple as updating the list (for example via an upstream node or configuration).
- The rest of the pipeline can remain the same, regardless of how many connections you have.
Best Practices
- Prefer name mode while designing and validating pipelines; switch to ID mode later for ultra-low latency when IDs are readily available.
- Keep expressions simple and readable; complex routing logic can be extracted to upstream nodes (e.g., Data Instance or JavaScript) that compute a
targetConnectionortargetFunction. - Combine Smart Connector with Condition, For-Each Loop, or Data Instance nodes to build powerful, dynamic routing and transformation flows with minimal duplication.