MQTT trigger node
MQTT Trigger Node
Overview
The MQTT Trigger Node automatically initiates MaestroHub pipelines when messages arrive on subscribed MQTT topics. Unlike the MQTT Subscribe connector node which receives messages within an already-running pipeline, the MQTT Trigger starts new pipeline executions in response to incoming messages—enabling fully event-driven automation.
Core Functionality
What It Does
MQTT Trigger enables real-time, event-driven pipeline execution by:
1. Event-Driven Pipeline Execution
Start pipelines automatically when MQTT messages arrive, without manual intervention or polling. Perfect for IoT sensor ingestion, command processing, and real-time data flows.
2. Automatic Subscription Management
Subscriptions are created and cleaned up automatically—no manual subscription management required.
3. Message Payload Passthrough
Incoming MQTT message payloads are passed directly to the pipeline, making them available to all downstream nodes via the $input variable.
Reconnection Handling
MaestroHub automatically handles connection disruptions to ensure reliable message delivery.
Automatic Recovery
When an MQTT connection is lost and restored:
- Connection Lost: The system detects the disconnection automatically
- Connection Restored: Subscriptions are automatically re-established within seconds
- Transparent Recovery: Pipelines continue to receive messages once the connection is restored—no manual intervention required
What This Means for Your Workflows
| Scenario | Behavior |
|---|---|
| Brief network interruption | Automatic resubscription after reconnection |
| Broker restart | Subscriptions automatically restored when broker comes back online |
| MaestroHub restart | All triggers for enabled pipelines are restored on startup |
To minimize message loss during brief outages, configure your MQTT Subscribe function with QoS 1 or QoS 2 and ensure your broker supports message persistence.
Configuration Options
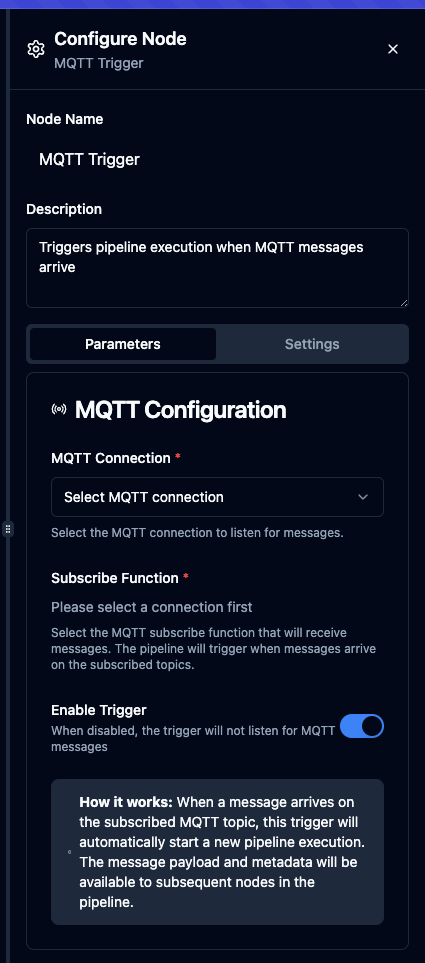
Parameters Configuration
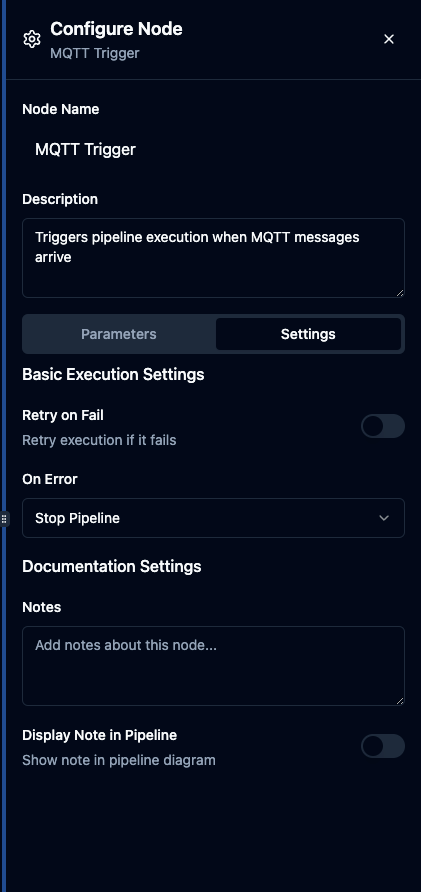
Settings Configuration
Basic Information
| Field | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Node Label | String (Required) | Display name for the node on the pipeline canvas |
| Description | String (Optional) | Explains what this trigger initiates |
Parameters
| Parameter | Type | Required | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Connection | Connection ID | Yes | - | The MQTT connection profile to use for subscribing |
| Function | Function ID | Yes | - | The MQTT Subscribe function that defines topic filters and subscription options |
| Enabled | Boolean | No | true | When disabled, the subscription is not created even if the pipeline is enabled |
The selected function must be an MQTT Subscribe function type. Publish functions cannot be used with MQTT Trigger nodes.
Settings
Basic Settings
| Setting | Options | Default | Recommendation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Retry on Fail | true / false | false | Keep disabled for triggers—retries don't apply to event-driven nodes |
| Error Handling | Stop Pipeline / Continue | Stop Pipeline | Use "Stop Pipeline" to halt on critical failures |
Documentation Settings
| Setting | Type | Default | Purpose |
|---|---|---|---|
| Notes | Text | Empty | Document the trigger's purpose, expected message formats, or operational context |
| Display Note in Pipeline | Boolean | false | Show notes on the pipeline canvas for quick reference |
Output Data Structure
When an MQTT message triggers pipeline execution, the following data is available to downstream nodes via the $input variable.
Output Format
{
"type": "mqtt_trigger",
"connectionId": "bf29be94-fc0a-4dc4-8e5c-092f1b74eb4b",
"functionId": "aef374c3-aa2b-454e-aabc-5657faac5950",
"enabled": true,
"node_id": "trigger.mqtt-1",
"message": "MQTT trigger provides configuration for event-based triggering",
"payload": {
"temperature": 23.5,
"unit": "celsius"
}
}
Accessing Message Data
In downstream nodes, use the $input variable to access the trigger output:
| Field | Expression | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Message Payload | $input.payload | The parsed MQTT message content (JSON object or raw value) |
| Connection ID | $input.connectionId | The MQTT connection profile used |
| Function ID | $input.functionId | The MQTT Subscribe function that received the message |
| Node ID | $input.node_id | The trigger node identifier |
| Trigger Type | $input.type | Always mqtt_trigger |
If your MQTT messages contain JSON, access nested fields directly:
$input.payload.temperature— Access a specific field$input.payload— Access the entire message object
Validation Rules
The MQTT Trigger Node enforces these validation requirements:
Parameter Validation
Connection ID
- Must be provided and non-empty
- Must reference a valid MQTT connection profile
- Error: "connectionId is required"
Function ID
- Must be provided and non-empty
- Must reference a valid MQTT Subscribe function
- Function must belong to the specified connection
- Error: "functionId is required"
Enabled Flag
- Must be a boolean if provided
- Error: "enabled must be a boolean"
Settings Validation
On Error
- Must be one of:
stopPipeline,continueExecution,retryNode - Error: "onError must be a valid error handling option"
Usage Examples
IoT Sensor Data Ingestion
Scenario: Process temperature readings from factory sensors in real-time.
Configuration:
- Label: Factory Temperature Monitor
- Connection: Production MQTT Broker
- Function: Subscribe to
sensors/temperature/#(all temperature topics) - Enabled: true
Downstream Processing:
- Parse JSON payload to extract temperature value
- Check if temperature exceeds threshold
- Send alert if threshold exceeded
- Store reading in time-series database
Command Processing
Scenario: Execute machine commands received from a central control system.
Configuration:
- Label: Machine Command Handler
- Connection: Control System MQTT
- Function: Subscribe to
commands/machine-01/+(all command types for machine-01) - Enabled: true
Downstream Processing:
- Validate command structure
- Route to appropriate PLC write node based on command type
- Log command execution result
- Publish acknowledgment to response topic
Multi-Plant Event Aggregation
Scenario: Aggregate events from multiple manufacturing plants for centralized monitoring.
Configuration:
- Label: Plant Event Aggregator
- Connection: Enterprise MQTT Broker
- Function: Subscribe to
plants/+/events/#(all events from all plants) - Enabled: true
Downstream Processing:
- Extract plant ID from topic
- Normalize event format
- Route critical events to alerting system
- Store all events in central data lake
Best Practices
Connection Health Monitoring
- Configure your MQTT connection with Keep Alive intervals appropriate for your network (default: 60 seconds)
- Enable Auto Reconnect on the connection profile for automatic recovery
- Monitor connection status through MaestroHub's connection health dashboard
Designing for Reliability
| Practice | Rationale |
|---|---|
| Use QoS 1 or 2 for critical messages | Ensures delivery acknowledgment and reduces message loss |
| Enable Clean Session = false (MQTT v3.1.1) or Session Expiry > 0 (MQTT v5.0) | Allows broker to queue messages during brief disconnections |
| Keep topic filters specific | Reduces unnecessary message processing and improves performance |
| Use wildcard topics judiciously | Broad wildcards (#) can result in high message volumes |
Error Handling Strategies
For Critical Workflows:
- Set On Error to
stopPipeline - Monitor pipeline execution failures
- Implement alerting for stopped pipelines
For Best-Effort Processing:
- Set On Error to
continueExecution - Log failed messages for later analysis
- Ensure downstream nodes handle partial failures gracefully
Performance Considerations
| Scenario | Recommendation |
|---|---|
| High message volume | Use specific topic filters; consider message batching in downstream nodes |
| Large payloads | Ensure adequate memory for payload processing; consider streaming for very large messages |
| Multiple triggers on same topic | MaestroHub optimizes this with shared subscriptions—no action needed |
| Burst traffic | Monitor pipeline execution queue; consider rate limiting in upstream systems |
Enable vs. Disable
- Use the trigger's Enabled parameter to temporarily pause message processing without changing pipeline state
- Disable triggers during maintenance windows to prevent message processing
- Document the reason for disabled triggers in the node's Notes field