Modbus Nodes
Modbus is the most widely deployed protocol in industrial automation. MaestroHub supports all three variants: TCP, RTU, and ASCII so you can communicate with PLCs, sensors, meters, and supervisory systems from a single node set.
Configuration Quick Reference
| Field | What you choose | Details |
|---|---|---|
| Parameters | Connection, Function, Function Parameters optional Timeout Override, Debug Mode | Choose the shared Modbus connection profile (credentials, transport method, retry settings) and its saved function, then fill in the parameters specified within the function. Inputs accept literal values or Maestro expressions that are validated at save time and resolved during each execution. |
| Settings | Retry on Fail, On Error, Notes, Display Note In Pipeline | Configure pipeline-level behavior: retry strategy, whether errors stop or continue, and operator notes that can surface on the canvas for quick context. |
Parameters inherit validation from the stored function, while node-level settings apply Maestro pipeline controls such as retries and inline documentation.

Modbus Read Node
Modbus Read Node
Read data from PLCs, sensors, meters, and industrial devices.
Supported Function Types:
| Function Name | Purpose | Common Use Cases |
|---|---|---|
| Read Coils (0x01) | Read digital outputs | Motor status, valve positions |
| Read Discrete Inputs (0x02) | Read digital inputs | Limit switches, sensors |
| Read Holding Registers (0x03) | Read holding registers | Setpoints, configuration |
| Read Input Registers (0x04) | Read input registers | Temperature, pressure, flow |
| Read FIFO Queue (0x18) | Read FIFO queue | Event logs, alarm history |

Modbus Write Node
Modbus Write Node
Write control values, setpoints, and configuration to devices.
Supported Function Types:
| Function Name | Purpose | Common Use Cases |
|---|---|---|
| Write Single Coil (0x05) | Write single digital output | Start/stop motor |
| Write Single Register (0x06) | Write single register | Update setpoint |
| Write Multiple Coils (0x0F) | Write multiple digital outputs | Batch control |
| Write Multiple Registers (0x10) | Write multiple registers | Configuration update |
| Write Masked Register (0x16) | Masked register write | Bit manipulation |
| Read/Write Multiple Registers (0x17) | Atomic read+write | Synchronized operations |
Always implement validation and safety checks before writing to industrial equipment. Consider adding condition nodes to verify values are within safe ranges.
Modbus Read Group Node
The Modbus Read Group node is an advanced connector node that allows you to execute multiple Modbus read operations efficiently within a single node. It provides powerful grouping capabilities and the Read All feature for comprehensive data collection.
Configuration
Connection and Functions
The Read Group node supports adding multiple function references, where each reference can either:
- Target a specific function from the connection
- Use Read All to execute all read functions associated with a connection
Read All Feature
The Read All toggle changes the behavior of a function reference:
| Mode | Description | Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| Specific Function (default) | Execute a single named function | Selective data collection from specific registers |
| Read All | Execute all read functions from the connection | Complete device data snapshot, monitoring dashboards |
How to Enable Read All
- Add a function reference in the Modbus Read Group node
- Toggle the Read All switch for that reference
- Optionally provide a Group Key (defaults to connection ID if not specified)
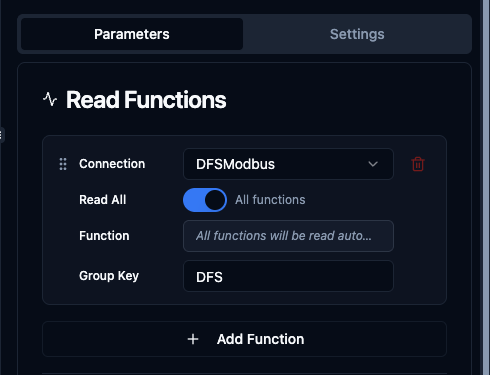
Read All toggle enabled - executes all read functions from the selected connection
When Read All is enabled:
- The function selector is hidden (not needed)
- All read functions (Read Coils, Read Discrete Inputs, Read Holding Registers, Read Input Registers) from the selected connection are executed
- Results are grouped under the specified group key or connection ID
Output Structure
{
"connectionId_or_groupKey": {
"function1_name": { /* function result */ },
"function2_name": { /* function result */ },
"function3_name": { /* function result */ }
}
}
Parameters
| Parameter | Description | Options |
|---|---|---|
| Execution Mode | How functions are executed | parallel (default), sequential |
| Continue on Error | Whether to continue if a function fails | true, false (default) |
| Functions | List of function references | Array of connection/function pairs |
Example Use Cases
Complete Device Snapshot
Use Read All when you need to collect all data points from a device for:
- Historical logging
- Complete device state export
- Dashboard population
- Diagnostic data collection
Selective Data Collection
Use specific functions when you need:
- Targeted data from specific registers
- Optimized performance (fewer operations)
- Precise control over what data is collected
Mixed Approach
Combine both modes in a single Read Group node:
- Read All from Connection A (complete data)
- Specific functions from Connection B (targeted data)
Execution Modes
Parallel Execution (Default)
- All functions execute concurrently
- Faster total execution time
- Best for independent read operations
- Use when functions access different address ranges
Sequential Execution
- Functions execute one after another
- More predictable timing
- Better for devices with limited concurrent request handling
- Use when device performance is a concern
Error Handling
Continue on Error = false (Default)
- Node fails if any function fails
- Ensures data consistency
- Best for critical operations where partial data is not acceptable
Continue on Error = true
- Node continues even if individual functions fail
- Failed functions return error in their result
- Best for monitoring scenarios where partial data is valuable
- Successful function results are still available in output
Best Practices
When to Use Read All
- Initial device commissioning and exploration
- Complete device state backups
- Dashboard views requiring all device data
- Diagnostic and troubleshooting scenarios
When to Use Specific Functions
- Production pipelines with known data requirements
- Performance-sensitive operations
- Selective data forwarding to specific systems
- When only a subset of device data is needed
Performance Considerations
- Read All executes all defined functions, which may impact performance on large function sets
- Consider using parallel execution mode for Read All to optimize speed
- Monitor device capabilities - some devices may have limits on concurrent requests
- Use Continue on Error strategically based on data criticality
Naming Conventions
- Use descriptive Group Keys when using Read All with multiple connections
- Group Keys help organize output data in complex pipelines
- Default connection ID grouping works well for simple scenarios